So, you’ve probably heard a lot about AI lately, right? Artificial Intelligence seems to be everywhere these days, from Siri on your iPhone to self-driving cars. But have you ever wondered what a weak example of AI looks like? Well, buckle up because we’re about to take a ride through the world of underwhelming artificial intelligence. Get ready to explore the limitations and shortcomings of AI systems that simply don’t measure up to our high expectations. Get ready to discover what separates the weak from the truly intelligent.
Types of Weak AI
Narrow AI (ANI)
Narrow AI, also known as Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI), refers to AI systems that are designed to perform a specific task or a narrow range of tasks. These AI systems are built to excel in a single domain and are not capable of generalizing their knowledge to other areas. For example, a chess-playing AI program that can defeat human opponents is a form of Narrow AI. While it may possess exceptional chess-playing abilities, it lacks the capability to engage in other intellectual activities.
Virtual Assistants
Virtual Assistants are one of the most common examples of Weak AI. These AI systems, such as Apple’s Siri and Amazon’s Alexa, are designed to interact with users and provide assistance with tasks such as scheduling appointments, answering questions, or playing music. Virtual Assistants rely on natural language processing and machine learning algorithms to understand and respond to user commands. While they may appear intelligent, they are limited in their capabilities and primarily function within the specified domain of their design.
Chatbots
Chatbots are another form of Weak AI that are widely used in customer support and online service interactions. These AI systems rely on natural language processing algorithms to engage in conversations with users and provide relevant information or assistance. Chatbots are often employed on websites or messaging platforms to simulate human-like interactions and provide instant responses to common queries. However, chatbots are generally programmed to handle specific scenarios and lack the ability to comprehend complex or nuanced inquiries.
Recommendation Systems
Recommendation systems are AI applications that analyze user preferences and behaviors to provide personalized suggestions or recommendations. These systems can be found in online platforms such as Netflix, Amazon, or Spotify, where they analyze user data, including past activities, ratings, and interactions, to generate tailored recommendations. While recommendation systems may seem intelligent in their ability to understand individual preferences, they are specialized algorithms designed for a specific purpose and lack general intelligence.
Image Recognition Tools
Image recognition tools are AI systems that utilize deep learning algorithms to classify and identify objects or patterns within images. These tools are commonly used in object identification, facial recognition, and autonomous driving technologies. While image recognition tools may exhibit impressive accuracy and speed in identifying objects, they are solely focused on analyzing visual data and lack the ability to comprehend other forms of information.
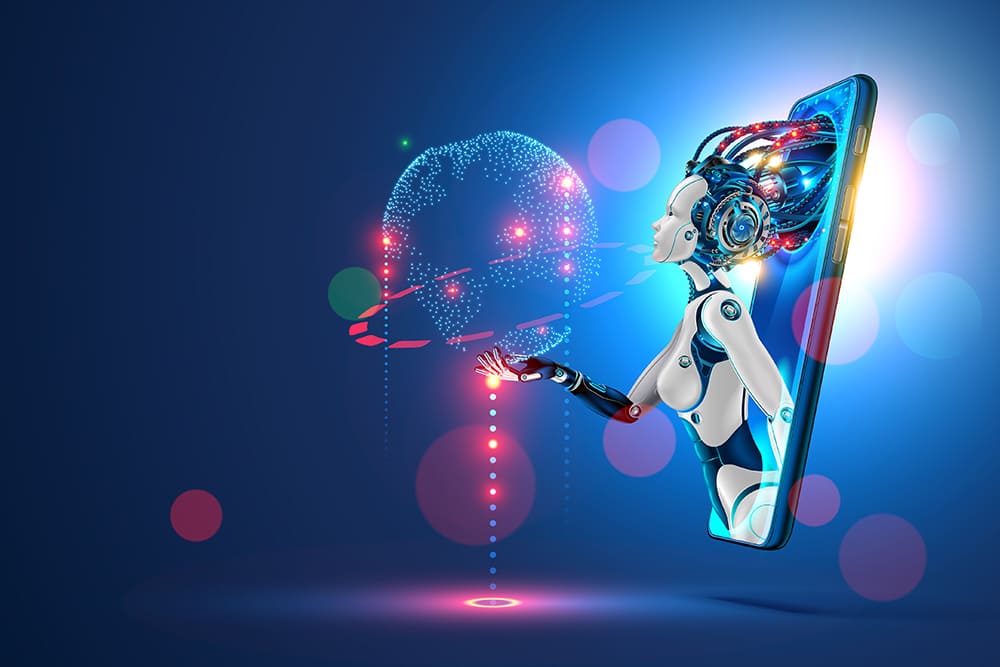

This image is property of bernardmarr.com.
Limitations of Weak AI
Lack of General Intelligence
One of the primary limitations of weak AI is its lack of general intelligence. Weak AI systems are designed to perform specific tasks within a narrow domain and lack the ability to apply their knowledge or skills outside that particular area. For example, a chess-playing AI program may excel at playing chess, but it has no understanding or capability to perform tasks unrelated to the game. Weak AI lacks the flexibility and adaptability of human intelligence, limiting its potential to address complex problems or engage in diverse activities.
Limited Scope of Expertise
While narrow AI exhibits exceptional capabilities within its designated domain, it is limited in terms of expertise. Weak AI systems are created to excel at a specific task or a restricted range of tasks, and they lack the breadth of knowledge and understanding that humans possess. For example, a medical diagnosis AI system may accurately identify symptoms and offer potential diagnoses, but it lacks the comprehensive medical knowledge and clinical experience of a human doctor. The narrow scope of expertise of weak AI systems restricts their ability to handle complex or ambiguous situations effectively.
Dependence on Training Data
Weak AI systems heavily depend on vast amounts of training data to learn and improve their performance. These systems are trained using datasets that are curated and labeled by humans, which can introduce biases or limitations in the training process. The accuracy and capabilities of weak AI are directly influenced by the quality and diversity of the training data it receives. If the training data is incomplete or biased, the AI system may produce inaccurate or unfair results. Additionally, weak AI systems may struggle to handle situations or inputs that deviate significantly from the training data, leading to errors or unexpected behavior.
Inability to Adapt to New Situations
Weak AI systems often struggle to adapt to new or unfamiliar situations that they were not explicitly trained for. While they can perform specific tasks within their designated domain, they lack the cognitive flexibility and problem-solving abilities to handle novel or unanticipated scenarios. For example, a language translation AI system may accurately translate text from one language to another, but it may fail to grasp the subtleties or context of the original message. Weak AI systems typically require extensive retraining or reprogramming to incorporate changes or adapt to new environments, making them less adaptable compared to humans.
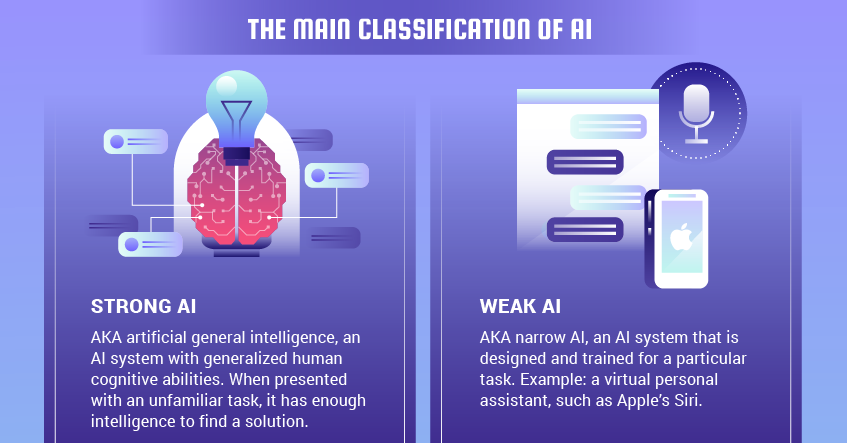
This image is property of miro.medium.com.
Ethical Concerns
Bias and Discrimination
One major ethical concern surrounding weak AI is the potential for bias and discrimination. Weak AI systems learn from vast amounts of training data, which can inadvertently introduce biases present in the data. These biases can manifest in various ways, such as racial or gender biases in facial recognition algorithms or discriminatory practices in hiring algorithms. If these biases are not identified and addressed, weak AI systems can perpetuate and amplify societal prejudices, leading to unfair treatment and discrimination.
Privacy and Security Risks
Weak AI systems often require access to large amounts of personal data to operate effectively. This raises concerns regarding privacy and data security. Users may be uncomfortable with AI systems collecting and analyzing their personal information, potentially leading to privacy breaches or misuse of sensitive data. Furthermore, weak AI systems can become targets for malicious actors, who may attempt to manipulate or exploit these systems for their own gain, posing significant security risks.
Human Replacement and Unemployment
As weak AI systems continue to advance and perform tasks previously performed by humans, there are concerns about job displacement and unemployment. While weak AI may excel in specific tasks, it lacks the comprehensive skills and capabilities of humans. Industries that heavily rely on repetitive or manual tasks, such as manufacturing, customer service, or transportation, may experience significant job loss as weak AI systems become more sophisticated. The ethical implications of widespread automation and potential unemployment raise important societal and economic concerns.
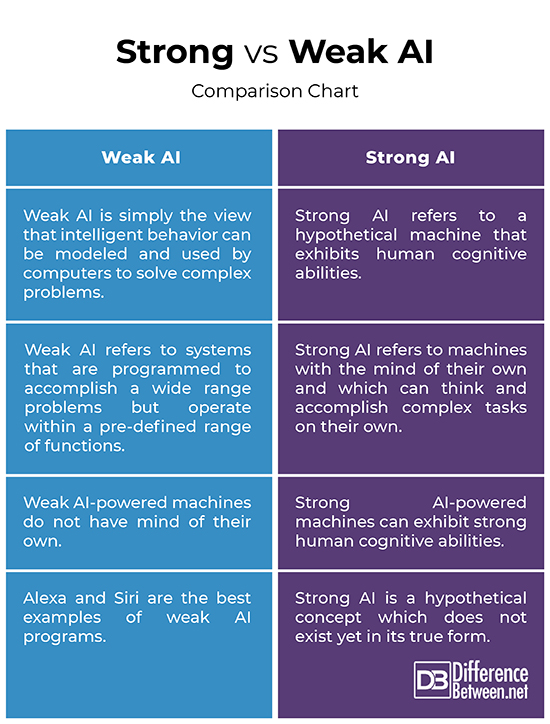
This image is property of cdn.differencebetween.net.
Examples of Weak AI Applications
Siri: Apple’s Virtual Assistant
Siri, Apple’s virtual assistant, is a popular example of weak AI. Siri is designed to understand and respond to voice commands, performing various tasks such as sending messages, setting reminders, or providing weather updates. While Siri can provide helpful information and assist with specific tasks, it operates within a narrow domain and lacks general intelligence. Siri’s primary function is to carry out pre-programmed tasks based on user input, rather than engage in complex, open-ended conversations or problem-solving.
Netflix: Personalized Recommendation System
Netflix utilizes a recommendation system powered by weak AI to generate personalized suggestions for its users. The recommendation system analyzes user data, including viewing history, ratings, and preferences, to provide tailored movie and TV show recommendations. While the recommendation system may appear intelligent in its ability to accurately predict user preferences, it operates within a specific domain and relies on algorithms that analyze patterns and similarities within the dataset. The weak AI behind Netflix’s recommendation system lacks the broader understanding and knowledge required for more nuanced recommendations.
Amazon Echo: Voice-Activated Smart Speaker
Amazon Echo, a voice-activated smart speaker powered by weak AI, is another prominent example. Users can interact with Amazon Echo by speaking commands and questions, and the device uses natural language processing and machine learning algorithms to understand and respond accordingly. Amazon Echo can perform tasks such as playing music, controlling smart home devices, and providing information. While Amazon Echo appears intelligent in its responses, it lacks the ability to comprehend complex inquiries or engage in deeper conversations.

This image is property of builtin.com.
Current Challenges and Future Possibilities
Improving Weak AI’s Learning Abilities
One of the current challenges in weak AI is enhancing its learning abilities to overcome limitations and improve performance. Researchers and developers are working on developing AI systems that can learn from smaller datasets, generalize knowledge across domains, and adapt to new situations more effectively. By incorporating advancements in deep learning, reinforcement learning, and transfer learning, weak AI can become more flexible and capable of applying acquired knowledge to a wider range of tasks and scenarios.
Enhancing Ethical Frameworks
Addressing ethical concerns surrounding weak AI is crucial for the responsible development and use of AI technologies. Efforts are being made to improve the transparency and accountability of AI systems, ensuring the fair and unbiased treatment of individuals. Developing robust ethical frameworks that guide the design, deployment, and use of weak AI can help mitigate risks such as bias, discrimination, and privacy breaches. Additionally, incorporating diverse perspectives and multidisciplinary collaborations can contribute to more comprehensive ethical guidelines.
Integration of Weak AI with Strong AI
The integration of weak AI with strong AI, also known as Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), presents exciting possibilities for the future. Strong AI refers to AI systems that possess human-like intelligence, capable of understanding, reasoning, and learning across various domains. By combining the specialized capabilities of weak AI with the broader intelligence of strong AI, it is possible to develop AI systems that excel in specific tasks while still demonstrating general intelligence. This integration may lead to advancements in fields such as healthcare, scientific research, and autonomous systems, enabling AI to tackle complex real-world challenges.
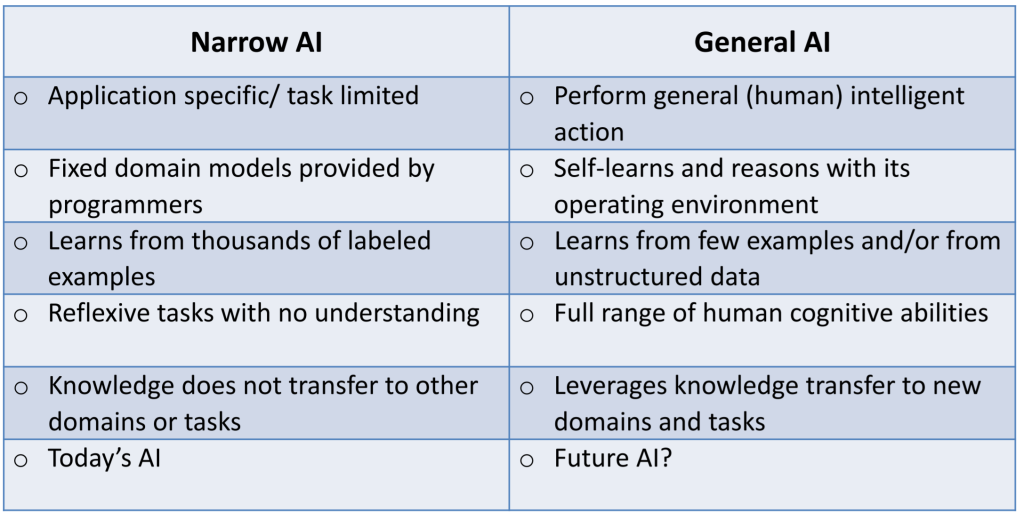
This image is property of www.techopedia.com.
