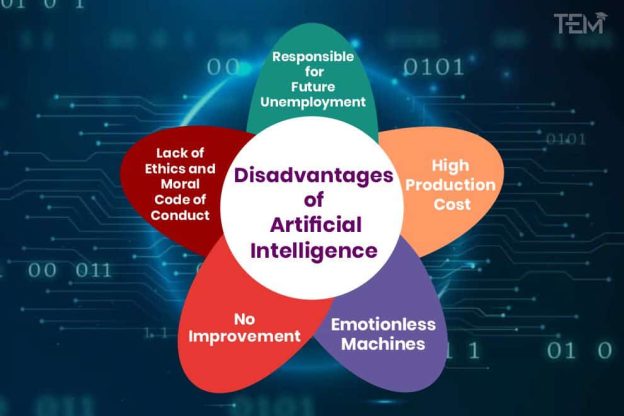
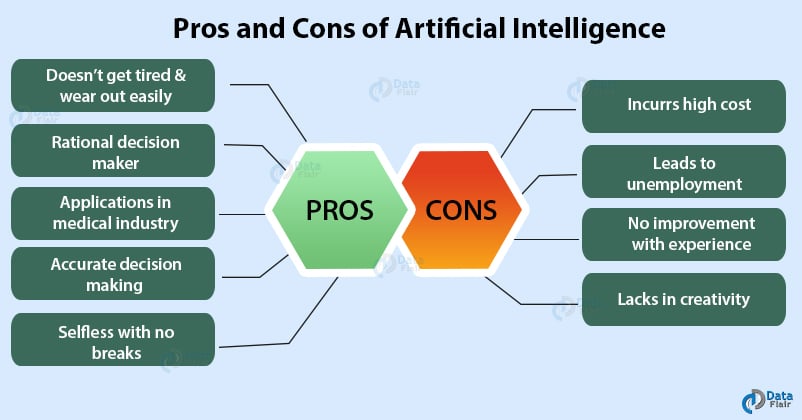
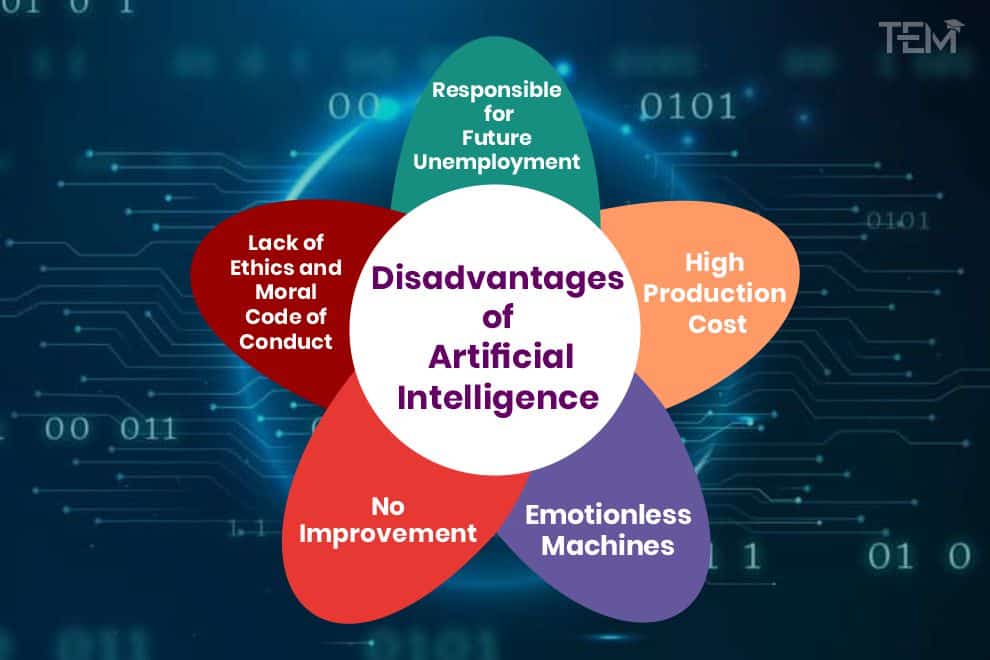
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming various industries, offering impressive advancements and possibilities. However, amidst its remarkable capabilities, there are certain drawbacks that need to be addressed. In this article, we will explore the top 5 drawbacks of artificial intelligence, shedding light on the potential risks and concerns surrounding this emerging technology. From job displacement to ethical dilemmas, it is crucial to have a comprehensive understanding of the challenges posed by AI to ensure its responsible and beneficial implementation in the future.
Job Displacement
Artificial intelligence (AI) has the potential to significantly impact the job market, leading to unemployment and a skills gap. As AI technology improves, certain roles that were once performed by humans may become automated, rendering many individuals unemployed. This displacement of workers can have severe consequences for both individuals and communities. People who lose their jobs due to AI may struggle to find employment in other fields, leading to financial instability and increased inequality.
Additionally, the skills required to thrive in a world heavily influenced by AI may differ from traditional job qualifications. This skills gap can be a barrier for individuals seeking employment in a rapidly evolving job market. Those who lack the necessary skills to adapt to AI-driven industries may find it challenging to secure stable and well-paying jobs, exacerbating existing socioeconomic disparities.
Furthermore, the rise of AI can lead to a loss of creativity in the workforce. While AI can process large amounts of data and perform tasks with great efficiency, it cannot replicate human creativity and innovation. As AI systems take over certain functions, there is a risk that critical thinking, problem-solving, and artistic expression may be overshadowed. This loss of creativity can have both cultural and economic implications, as the human touch and unique perspective are often vital in various fields, such as art, design, and marketing.
Privacy Concerns
The advancement of AI technology raises significant concerns regarding privacy. Data breaches are becoming increasingly common as AI systems collect vast amounts of personal and sensitive information. These breaches can result in the exposure of personal data, leading to identity theft, fraud, and other forms of cybercrime. As AI systems become more intertwined with our daily lives, protecting personal information becomes a crucial challenge.
Furthermore, the proliferation of AI can lead to increased surveillance. AI-powered surveillance systems have the capability to monitor individuals’ actions, choices, and even emotions. This level of surveillance raises concerns about privacy infringement and the potential for abuse by governments, corporations, or other entities. The widespread use of AI surveillance systems can create a society where individuals are constantly under scrutiny, eroding personal freedoms and creating a chilling effect on behaviors and opinions.
This image is property of data-flair.training.
Automation Bias
One of the drawbacks associated with AI is the tendency towards overreliance and trust in automated systems. Automation bias refers to the human tendency to unquestioningly trust the decisions and recommendations made by AI systems. This blind trust can lead to complacency, where humans become passive observers instead of actively engaging with the technology.
Automation bias can be particularly problematic when AI systems make errors. While AI has the potential to improve accuracy and efficiency, it is not infallible. Errors can occur due to flawed algorithms, inadequate training data, or unforeseen circumstances. Overreliance on AI systems can lead humans to overlook these errors or fail to notice when the technology is producing incorrect or biased results. Such errors can have significant consequences in critical sectors such as healthcare, finance, or transportation, where incorrect decisions can lead to harm or loss of life.
Ethical Issues
Artificial intelligence introduces a range of ethical concerns that need to be addressed. One such issue is the lack of accountability in AI systems. As AI operates based on algorithms and complex decision-making processes, it can be challenging to determine who should be held responsible for the outcomes of AI-generated decisions. This lack of clear accountability can lead to potential injustices or unfair outcomes, especially when AI systems are involved in high-stakes decision-making, such as in criminal justice or hiring processes.
Furthermore, bias and discrimination can be inadvertently perpetuated by AI systems. If the training data used to build AI models contains biases, these biases can be replicated and amplified in the system’s decision-making process. For instance, AI used in facial recognition software has been found to have higher error rates for certain racial or ethnic groups, leading to biased outcomes and potential discrimination.
This image is property of www.theeducationmagazine.com.
Safety Risks
While AI has the potential to improve safety in various domains, it also introduces new safety risks. One concern is the possibility of malfunctions in AI systems. Despite rigorous testing and development, AI systems can still encounter technical issues that lead to errors or unexpected behaviors. These malfunctions can have far-reaching consequences in sectors that rely heavily on AI, such as autonomous vehicles or critical infrastructure. Ensuring the safety and reliability of AI systems requires diligent monitoring, maintenance, and a comprehensive understanding of potential failure modes.
Another safety risk associated with AI is the lack of human judgment. While AI systems can process vast amounts of data and analyze complex scenarios, they may struggle to exhibit the same level of judgment and intuition as humans. In situations where human judgment is crucial, such as in emergency response or ethical decision-making, an overreliance on AI systems may result in suboptimal or even dangerous outcomes.
Limited Emotional Intelligence
Emotional intelligence, the ability to perceive, understand, and manage emotions effectively, is a uniquely human trait that presents challenges for AI systems. Although AI algorithms can analyze and interpret data related to emotions, they often struggle to truly understand and empathize with human emotions. This limited emotional intelligence can be problematic in various social contexts, such as customer service or healthcare, where empathy and emotional connection are vital for human interaction.
Furthermore, AI systems may misinterpret emotions or fail to recognize subtle cues that humans easily perceive. These misinterpretations can lead to misunderstandings or inappropriate responses, especially in situations that require nuanced understanding, such as negotiations, therapy, or conflict resolution. The lack of emotional intelligence in AI systems can hinder effective communication and human-like interactions, limiting their potential usefulness in certain areas.
This image is property of static.javatpoint.com.
Unpredictable Decision-Making
The decision-making processes of AI systems can often seem opaque or unpredictable, posing challenges for transparency and accountability. AI algorithms can be complex and multi-layered, making it difficult for humans to fully understand how and why a particular decision or recommendation was reached. This lack of transparency can erode trust in AI systems and hinder their acceptance in critical decision-making domains.
Furthermore, AI decision-making may fall short compared to human judgment in certain situations. Human decision-making often incorporates intuition, situational context, and ethical considerations that are challenging to replicate in AI systems. While AI can analyze vast amounts of data and detect patterns, it may struggle to make judgments based on nuanced or subjective factors. As a result, AI decision-making may be inferior or out of touch with human values, potentially leading to suboptimal outcomes.
Cost and Accessibility
The development and implementation of AI technology can be expensive, creating barriers for access in certain contexts. Building and training sophisticated AI systems require significant financial investment, making it challenging for small businesses, startups, or individuals to enter the field. The high cost of AI development can exacerbate inequalities, as only those with sufficient resources can leverage the advantages offered by AI technology.
Inequitable access to AI technology can also lead to disparities in opportunities. Organizations or individuals with limited resources may find it difficult to compete in a world increasingly reliant on AI systems. This can result in further concentration of power and resources, creating a digital divide between those who have access to the benefits of AI and those who do not.
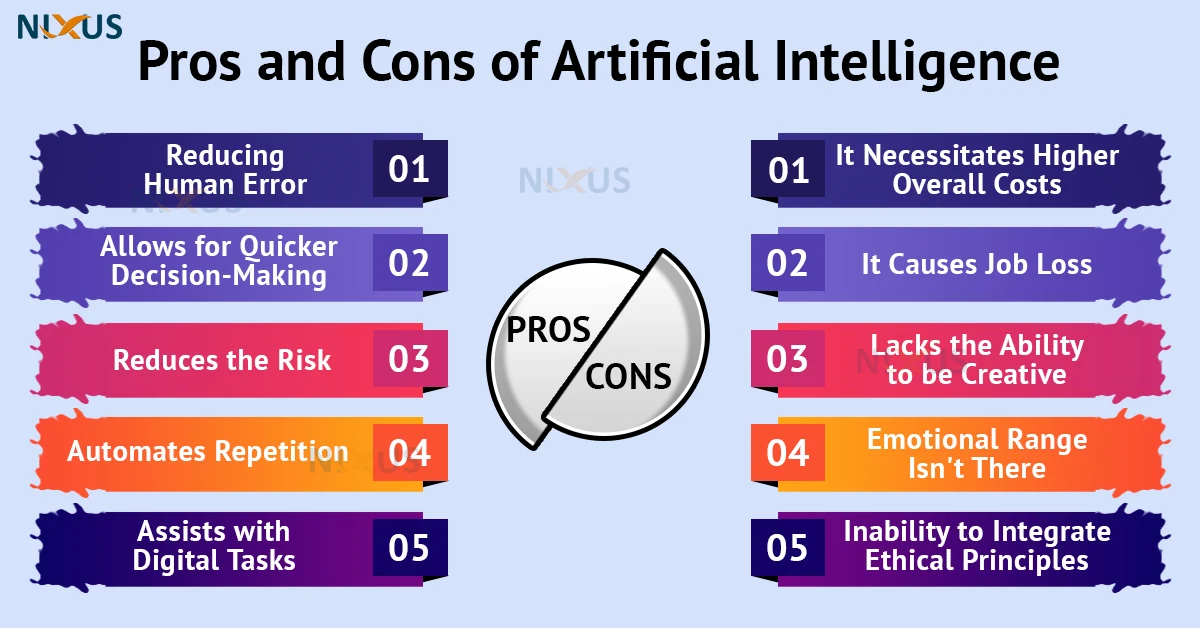
This image is property of nixustechnologies.com.
Dependence on Technology
As AI technology becomes more advanced and prevalent, there is a growing concern about our increasing dependence on it. Reliance on AI systems for critical functions, such as decision-making or infrastructure management, can create vulnerabilities. Technical failures, cyberattacks, or system malfunctions can have far-reaching consequences if humans are ill-prepared to handle such situations without the aid of AI. Moreover, the extensive integration of AI into various aspects of our lives may diminish our ability to maintain control and agency over important aspects of our existence.
Additionally, dependence on AI raises concerns about the loss of skills and knowledge that were once essential for human survival. As AI systems take over tasks and responsibilities traditionally performed by humans, there is a risk that certain skills, such as problem-solving, critical thinking, or manual dexterity, may deteriorate due to lack of practice. This loss of skills can have long-term consequences for individuals and society as a whole.
Potential for Job Restrictions
Perhaps one of the most significant drawbacks of AI is the potential for job restrictions. As AI technology continues to advance, it may surpass human capabilities in various domains. While this can lead to increased efficiency and improved outcomes, it also raises concerns about the limited opportunities available for human workers. AI systems that can outperform humans in tasks previously considered the domain of human expertise may result in a significant reduction in job opportunities for individuals in those fields, leading to unemployment and a shift in the labor market.
Moreover, as AI systems become more sophisticated, they may not only replace manual labor but also encroach upon roles that require complex cognitive skills. This can have far-reaching implications for professionals in fields such as law, medicine, or finance, where AI systems have the potential to outperform humans in data analysis, research, or decision-making. The potential for job restrictions creates a need for individuals to adapt and acquire new skills to remain relevant in an AI-driven job market.
In conclusion, while artificial intelligence offers numerous benefits and opportunities, it also presents a range of drawbacks and challenges. Job displacement, skills gap, loss of creativity, privacy concerns, automation bias, ethical issues, safety risks, limited emotional intelligence, unpredictable decision-making, cost and accessibility, dependence on technology, and potential job restrictions are some of the key concerns associated with the increasing implementation of AI. Addressing these drawbacks will require careful consideration, robust regulations, and proactive efforts to ensure that AI technology is developed and deployed responsibly, ethically, and in ways that benefit society as a whole.

This image is property of www.aplustopper.com.