So you’ve heard about AI marketing, the innovative use of artificial intelligence in marketing strategies. It’s undoubtedly transforming the way businesses connect with consumers, but have you ever considered the ethical implications behind this technology? In this article, we’ll explore the potential ethical issues that arise when AI is integrated into marketing practices. From privacy concerns to biased algorithms, we’ll delve into the ethical challenges that marketers face in leveraging AI to reach their target audience. Let’s take a closer look and unravel the ethical complexities of AI marketing.
Ethical Issues with AI Marketing
AI marketing, also known as artificial intelligence marketing, is the use of AI technology to analyze customer data and deliver personalized marketing experiences. While AI marketing has the potential to improve customer segmentation, targeting, and engagement, it also raises several ethical concerns. In this article, we will explore the most significant ethical issues associated with AI marketing and discuss their implications for businesses and society as a whole.
Privacy Concerns
One of the foremost ethical issues with AI marketing revolves around privacy concerns. AI marketing algorithms collect vast amounts of personal data from individuals, including their browsing history, online purchases, social media activities, and location information. This data, when misused or mishandled, can potentially infringe upon an individual’s privacy and compromise their personal information.
The use of AI in marketing requires transparency and informed consent from consumers. People should have control over how their data is collected, used, and shared. However, the complexity of AI algorithms often makes it challenging for consumers to understand the extent to which their data is being used, resulting in a lack of transparency and potential violation of privacy rights.
Data Accuracy and Bias
Another significant ethical concern in AI marketing is the issue of data accuracy and bias. AI algorithms rely heavily on large data sets to identify patterns and make predictions. However, if these data sets contain biases or inaccuracies, it can lead to biased decision-making and discrimination.
For example, if an AI marketing algorithm is trained on data that represents a certain demographic more than others, it may result in preferential treatment or exclusion of specific groups. This can perpetuate discriminatory practices and reinforce societal biases. Furthermore, inaccurate data can lead to incorrect targeting and messaging, which can ultimately harm brands and alienate consumers.
This image is property of d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net.
Manipulation and Deception
AI marketing has the potential to manipulate and deceive consumers by using sophisticated algorithms to deliver personalized messages. By leveraging vast amounts of data on consumer preferences, behaviors, and vulnerabilities, AI algorithms can target individuals with highly persuasive advertisements, driving them towards certain products or actions.
Such manipulation raises ethical concerns as it exploits consumers’ weaknesses and restricts their freedom of choice. It blurs the line between personalization and manipulation, potentially eroding trust in marketing practices. To address this issue, businesses must strive for transparency and ensure that AI algorithms are used responsibly, with a focus on empowering consumers rather than deceiving them.
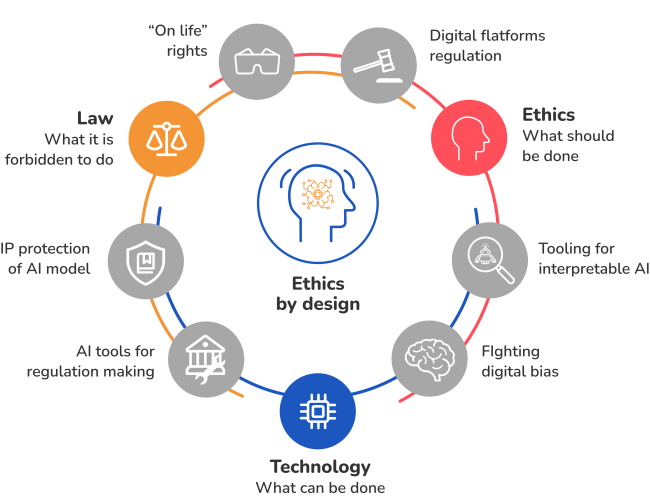
Lack of Transparency
Transparency is a critical aspect of ethical AI marketing. However, due to the complexity of AI algorithms, their inner workings can often be opaque and difficult to understand. This lack of transparency poses challenges for marketers, consumers, and regulators alike.
Consumers have a right to know how AI algorithms make decisions that affect their lives, such as the ads they are shown or the prices they are charged. Without transparency, consumers may feel exploited or manipulated, leading to decreased trust in AI-driven marketing strategies. Similarly, marketers need transparency to ensure that AI algorithms are not inadvertently biased or making unethical decisions.
This image is property of d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net.
Algorithmic Discrimination
Algorithmic discrimination refers to the potential biases and discrimination that can be perpetuated by AI algorithms. AI marketing algorithms rely on data to make decisions, and if this data contains biases or discriminatory patterns, it can lead to unjust outcomes.
For instance, if an AI algorithm is trained on data that predominantly represents a specific gender or race, it may result in the unfair targeting or exclusion of certain groups. This can perpetuate societal inequalities and reinforce harmful stereotypes. It is crucial for businesses to consider these ethical implications and actively work towards addressing algorithmic discrimination in AI marketing.
Unaccountability and Responsibility
One of the challenges with AI marketing is the issue of accountability and responsibility. AI algorithms make decisions autonomously based on their training data, making it difficult to assign responsibility for any unethical or harmful outcomes.
In traditional marketing, if a company engages in deceptive practices, there are legal and ethical consequences. However, in AI marketing, responsibility becomes murky, as decisions are made by algorithms rather than individuals. This lack of accountability raises concerns about who is responsible for the ethical implications of AI marketing and how companies can be held accountable for any harms caused.
This image is property of www.orientsoftware.com.
Loss of Human Connection
While AI marketing enables personalized and targeted experiences for consumers, it also runs the risk of diminishing the human connection between brands and customers. By relying solely on data analytics and algorithms, businesses may overlook the importance of genuine human interaction in building trust and loyalty.
Customers value authentic relationships with brands, and AI-driven marketing tactics that eliminate human touchpoints can leave consumers feeling disconnected or undervalued. Businesses must strike a balance between leveraging AI technology and maintaining meaningful human connections to ensure ethical marketing practices.
Unfair Competition and Monopolization
The use of AI in marketing can potentially exacerbate the issue of unfair competition and monopolization. As AI algorithms become more sophisticated, they can provide companies with a competitive advantage by enabling them to analyze massive amounts of data and make real-time decisions.
Smaller businesses or those with limited access to resources may struggle to compete with larger organizations that can afford advanced AI marketing tools. This concentration of power in the hands of a few can stifle innovation and potentially lead to market monopolization. Ensuring a level playing field and fair competition in the AI marketing landscape is vital to maintain an ethical business environment.
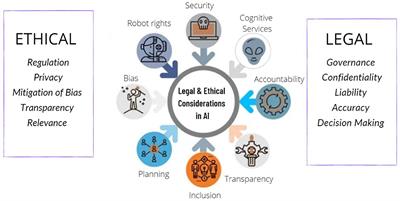
This image is property of www.frontiersin.org.
Unintended Consequences
AI marketing, like any technology, can have unintended consequences that are difficult to anticipate. While AI algorithms are designed to optimize marketing strategies and enhance customer experiences, they can sometimes result in unforeseen negative impacts.
For example, an AI algorithm might inadvertently target vulnerable individuals with harmful content or inadvertently promote harmful products. This lack of control over unintended consequences raises ethical concerns and emphasizes the need for ongoing monitoring, evaluation, and adaptation of AI marketing strategies to mitigate potential risks.
Ethical Decision-making in AI Marketing
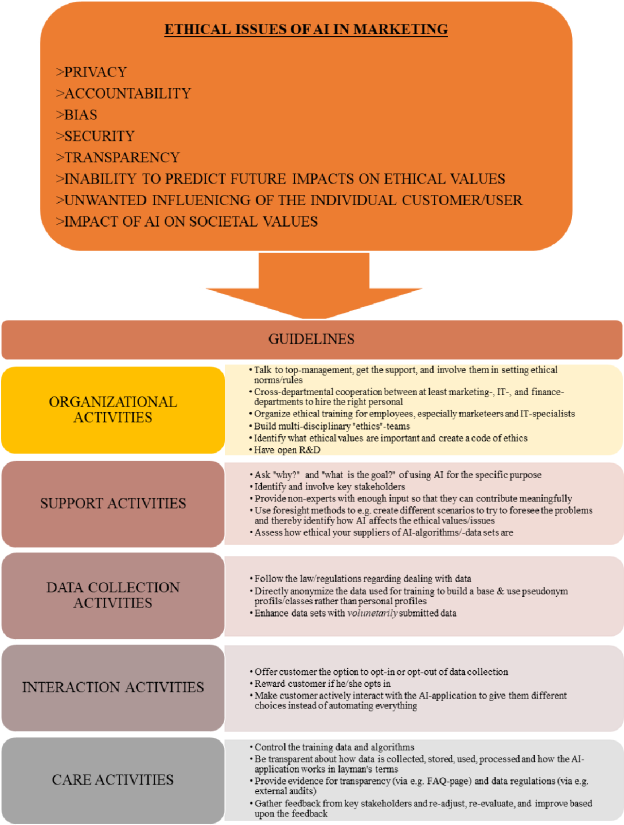
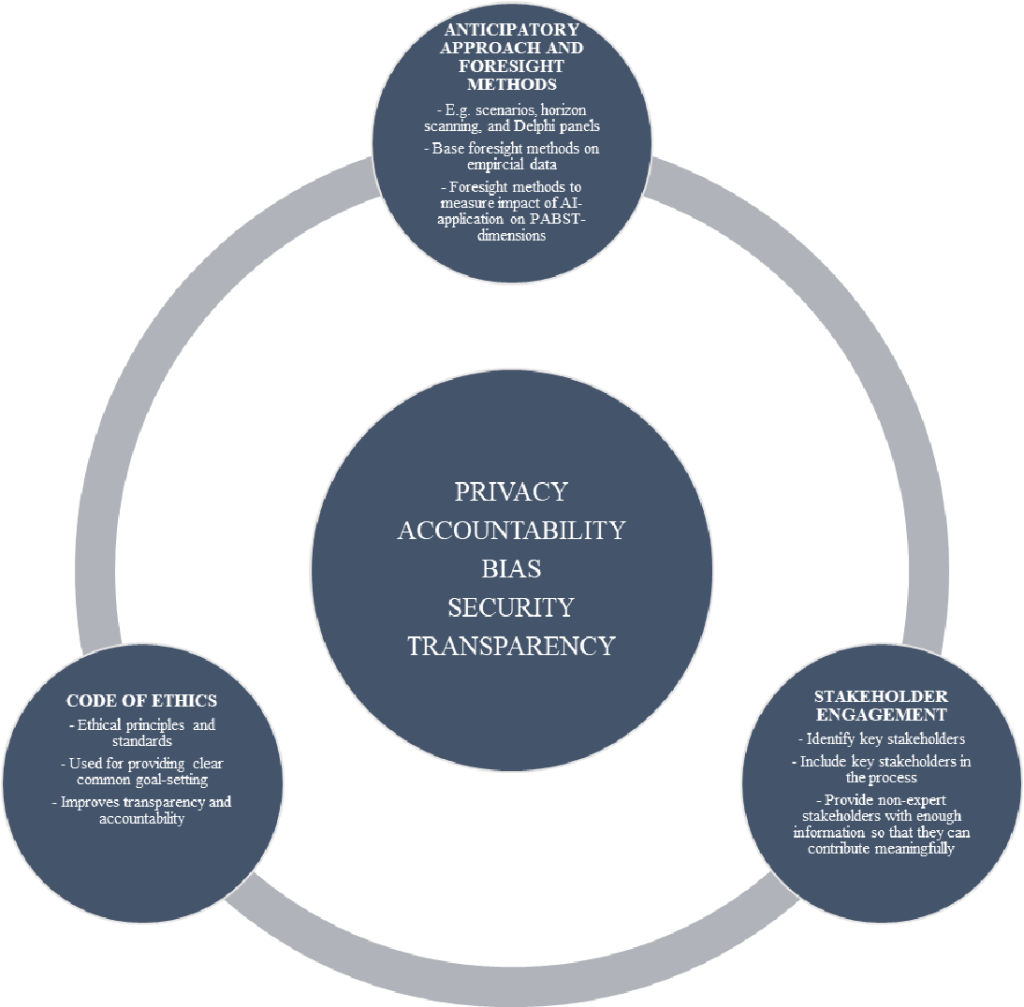
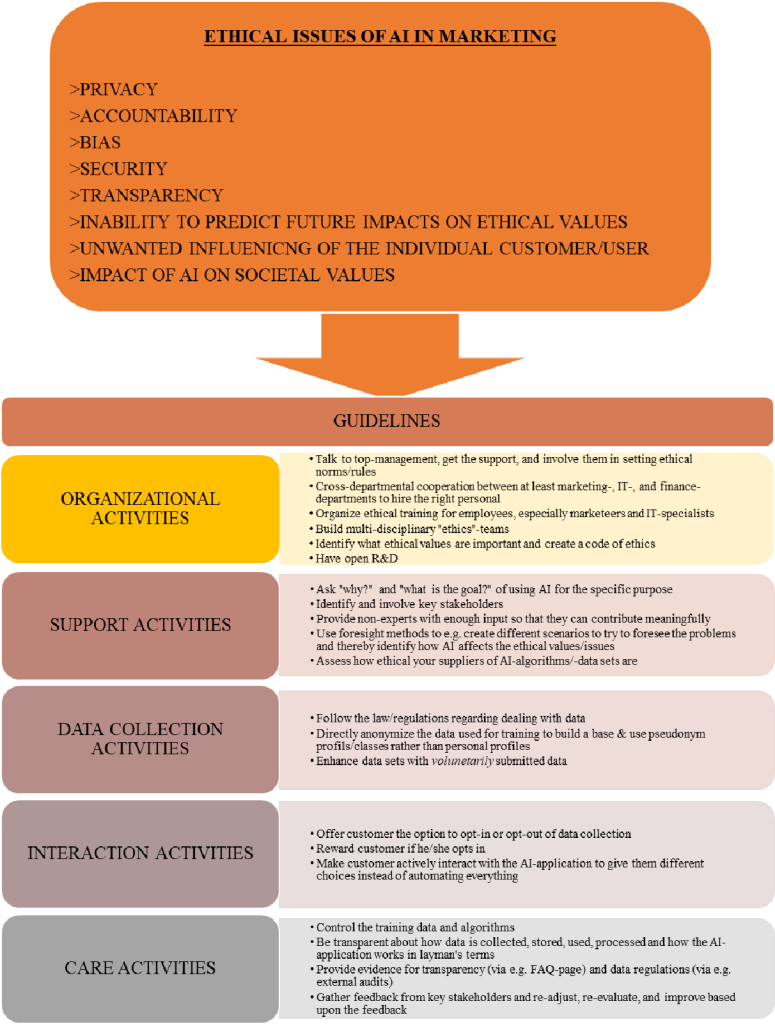
To address the ethical issues associated with AI marketing, businesses must prioritize ethical decision-making frameworks. Companies should consider the following principles when designing AI-driven marketing strategies:
- Transparency: Ensuring transparency in data collection, algorithmic decision-making, and use of personal information.
- Data ethics: Evaluating and mitigating biases in data sets to prevent algorithmic discrimination.
- Informed consent: Obtaining explicit consent from consumers before using their personal data for marketing purposes.
- Human oversight: Maintaining human involvement in decision-making processes to prevent excessive reliance on AI algorithms.
- Accountability: Establishing mechanisms to assign responsibility for AI marketing outcomes and addressing any harms caused.
- Continual monitoring and evaluation: Regularly assessing the impacts of AI marketing strategies and adapting them to mitigate potential risks and unintended consequences.
- Customer empowerment: Empowering customers to have control over their personal data, providing opt-out options, and enabling informed choices.
By adopting these ethical principles, businesses can navigate the complex landscape of AI marketing, build consumer trust, and ensure the responsible and ethical use of AI technology.
In conclusion, AI marketing presents several ethical challenges that require careful consideration. Privacy concerns, data accuracy and bias, manipulation and deception, lack of transparency, algorithmic discrimination, unaccountability, loss of human connection, unfair competition, and unintended consequences are all significant ethical issues associated with AI marketing. By integrating ethical decision-making frameworks into AI marketing strategies, businesses can promote responsible and ethical practices while harnessing the potential benefits of AI technology.

This image is property of miro.medium.com.