So, you’ve heard all the buzz about AI and how it’s revolutionizing various industries. It’s undeniably impressive how this technology can learn, adapt, and perform tasks that were once exclusive to humans. However, amidst all the excitement, there is a pressing question that needs to be addressed: what is the biggest con of AI? While AI undoubtedly has its merits, it also brings forth a significant concern – the potential loss of jobs. As AI continues to evolve and improve, there is a growing fear that it may replace human workers, leading to widespread unemployment and socioeconomic consequences. The question then becomes, how can we strike a balance between reaping the benefits of AI and preserving human livelihoods? AI, or Artificial Intelligence, has undoubtedly revolutionized various aspects of our lives. From enhancing efficiency in industries to improving healthcare, AI has demonstrated its potential to augment human capabilities. However, it is important to recognize that AI is not without its drawbacks. In this article, we will explore some of the most significant concerns surrounding AI, ranging from job displacement to the potential risks of autonomous weapons.

Job Displacement
Increasing Unemployment Rates
One of the major concerns associated with AI is the increasing unemployment rates it may contribute to. As AI systems become more advanced and capable, there is a growing fear that they will replace human workers in various industries. While automation has been a part of industrial progress throughout history, the rate at which AI is evolving raises concerns that many individuals may find their jobs at risk.
Loss of Specialized Jobs
Furthermore, AI’s ability to learn and adapt can potentially lead to the loss of specialized jobs. Certain professions that require years of training and expertise may be rendered obsolete as AI systems become proficient in performing those tasks. This not only affects the individuals whose livelihoods depend on these specialized jobs but also risks eroding the depth of knowledge and experience that humans bring to those fields.
Unequal Distribution of Job Opportunities
Moreover, the widespread adoption of AI may lead to an unequal distribution of job opportunities. Those with the necessary skills and resources to work alongside AI systems will thrive, while others may face limited employment prospects. This can exacerbate existing social and economic disparities, further deepening inequality within societies.
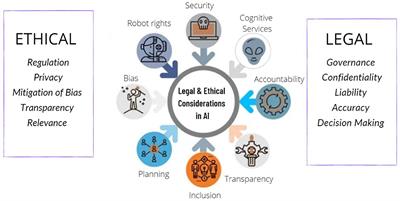
Ethical Concerns
Lack of Transparency and Accountability
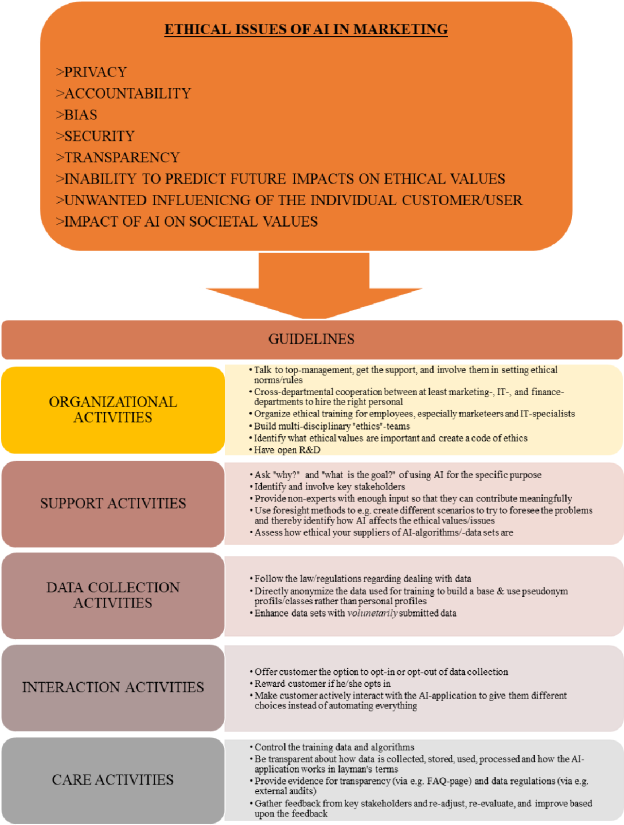
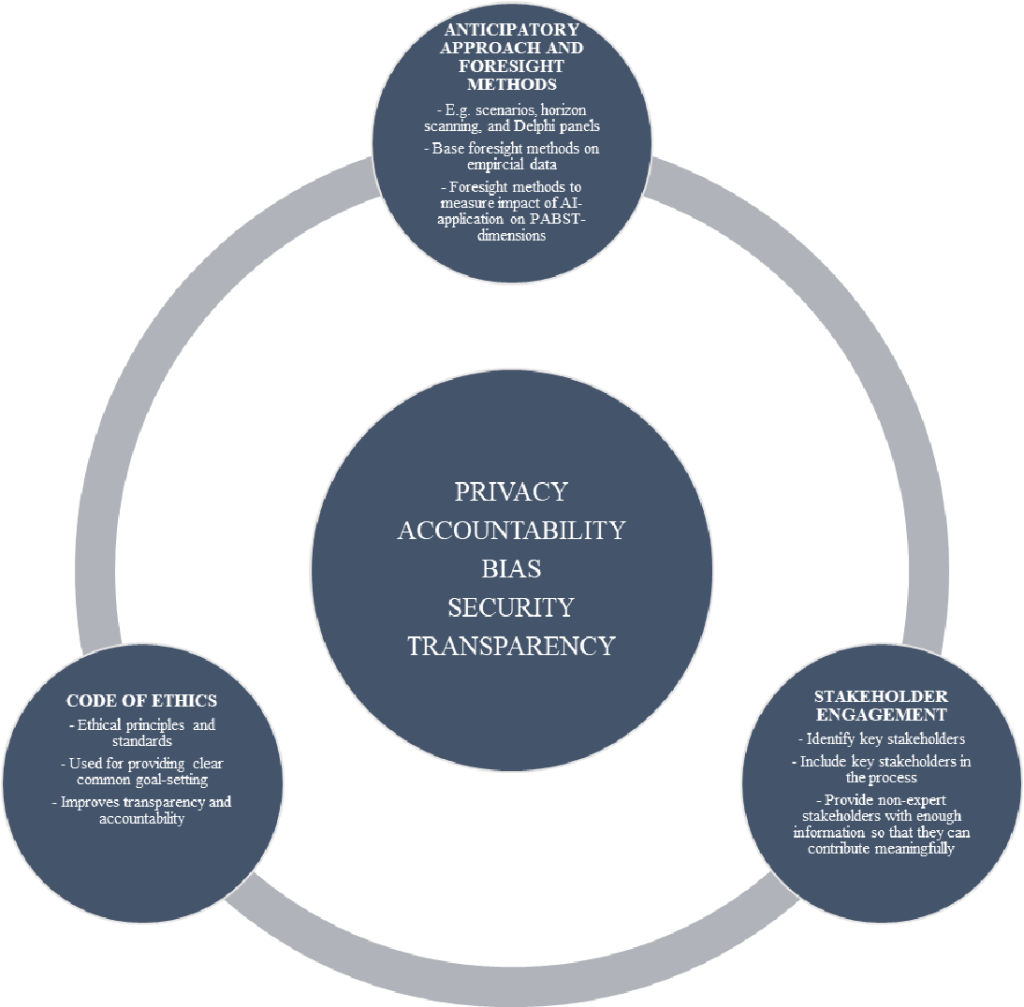
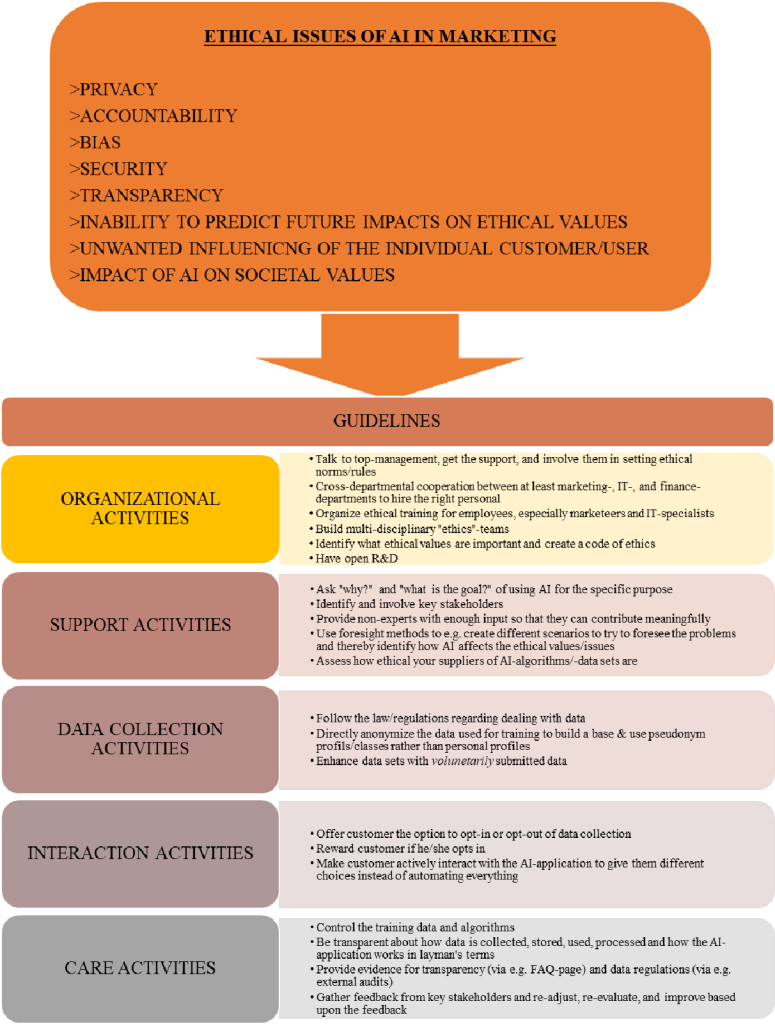
Another significant concern surrounding AI is the lack of transparency and accountability in its decision-making processes. AI algorithms can be complex and difficult to understand, raising questions about how these systems make crucial decisions. Without transparent processes, it becomes challenging to identify and rectify biased or discriminatory outcomes, potentially perpetuating injustices.
Bias in Algorithms
Bias in AI algorithms is another ethical concern. AI systems learn from data, and if that data is biased or reflects societal prejudices, the AI can inadvertently reinforce those biases. For example, AI used in recruitment processes may inadvertently favor certain demographics or perpetuate gender or racial biases present in historical hiring data. Addressing and mitigating algorithmic bias is crucial to ensuring fair and equitable AI systems.
Data Privacy and Security
With AI relying heavily on data, concerns about data privacy and security are paramount. As AI systems collect and analyze vast amounts of personal information, there is a risk of unauthorized access or misuse of data. Safeguarding individual privacy becomes increasingly challenging when AI systems are involved, raising important ethical questions about data ownership, consent, and protection.
Unintended Consequences
Lastly, the potential for unintended consequences is a significant ethical concern. The complexity of AI systems makes it difficult to predict all possible outcomes and impacts. Unintended consequences may arise when AI systems operate in complex and dynamic environments, potentially leading to unexpected results that could have significant social, economic, or even safety consequences.
Dehumanization
Reduced Human Interaction
AI’s advancement also raises concerns about reduced human interaction. As AI systems become more capable of performing tasks traditionally done by humans, interpersonal interactions might decrease. This can have consequences on personal relationships, customer service experiences, and overall quality of life, as human connection and empathy are often vital components of our well-being.
Loss of Empathy and Emotional Connection
Moreover, the reliance on AI systems may diminish our ability to empathize and emotionally connect with others. AI lacks the capacity to truly understand and experience human emotions, making it incapable of providing genuine emotional support or empathetic responses. Over time, the decrease in meaningful human interactions may impact our collective emotional intelligence and human connection.
Dependence on AI for Decision-Making
AI’s rapid development also brings forth concerns about the extent to which we rely on AI systems for decision-making. While AI can assist in processing vast amounts of information and providing recommendations, placing too much trust in these systems may reduce our personal autonomy and critical thinking abilities. Blindly following AI-generated decisions without considering the broader context and ethical implications can be problematic.
Diminished Personal Autonomy
Lastly, the increasing integration of AI in our daily lives can lead to diminished personal autonomy. Autonomous systems and AI-powered technologies can influence our behaviors and choices, potentially limiting our freedom and agency. Whether it is in consumer choices, healthcare recommendations, or even political decision-making, the influence of AI on personal autonomy deserves careful consideration.
Negative Impact on Productivity
Reliance on AI Can Hinder Creativity and Innovation
While AI can enhance productivity in certain areas, an over-reliance on AI systems can potentially hinder creativity and innovation. Relying solely on AI-generated ideas and solutions may stifle human ingenuity and limit the exploration of unconventional approaches. Maintaining a balance between AI-driven optimizations and human creativity is essential to foster continued growth and advancement.
Technical Failures and System Vulnerabilities
Another concern is the susceptibility of AI systems to technical failures and vulnerabilities. AI systems are not immune to errors, and their reliance on complex algorithms and infrastructure means that failures can occur. Whether it is system malfunctions, hacking, or manipulation of AI models, the potential for technical failures and vulnerabilities introduces risks that can have far-reaching consequences, from disrupted services to compromised data integrity.
Time-consuming Adjustments and Learning Curves
Adopting and integrating AI systems can consume significant time and resources. The learning curve associated with implementing AI technology, training employees, and adapting existing workflows can be steep. This can temporarily impact productivity as organizations navigate the adjustments and fine-tuning required to fully leverage AI’s potential. Neglecting these transitional challenges can impede the expected gains in productivity.

Unequal Access to AI
Economic Disparities Limit AI Adoption
One of the prominent concerns regarding AI is the unequal access to its benefits. High costs associated with AI development, implementation, and maintenance may restrict access to larger corporations or affluent organizations. This can perpetuate existing economic disparities, leaving smaller businesses and individuals with limited resources at a disadvantage, impeding their ability to compete and grow in an AI-driven world.
Education and Technology Divide
Additionally, the education and technology divide can exacerbate the unequal access to AI. Access to quality education and opportunities for technological skill development is crucial for individuals to participate in the AI-powered economy. However, disparities in educational systems and limited access to resources can widen the gap, leaving certain demographics and regions behind in terms of AI adoption and the potential benefits it offers.
Concentration of Power in Few Hands
Furthermore, the widespread adoption of AI raises concerns about the concentration of power in the hands of a few dominant players. Companies that possess the resources and capabilities to develop and deploy AI systems at scale can gain significant advantages. This concentration of power and influence can limit competition, stifle innovation, and potentially lead to unfair market dynamics that disadvantage smaller players and hinder economic growth.
Social Inequality
Accumulation of Wealth for AI Developers and Companies
The development and deployment of AI systems have the potential to accumulate substantial wealth for AI developers and companies. As AI permeates various industries, those at the forefront of AI research and development may amass significant financial gains. This concentration of wealth can contribute to widening social and economic inequalities unless appropriate mechanisms are in place to distribute the benefits of AI more equitably.
Exacerbating Existing Social and Economic Divisions
Moreover, AI has the potential to exacerbate existing social and economic divisions. If certain industries or regions embrace AI more rapidly than others, it can result in localized economic disparities. Communities that are unable to adapt or access AI-driven opportunities may be left behind, amplifying social and economic inequalities and creating a significant divide within society.
Automation Favoring Certain Industries or Demographics
The automation enabled by AI technology may also favor certain industries or demographics over others. Jobs that are easily automated, such as routine tasks in manufacturing, are more susceptible to displacement. This can disproportionately impact individuals working in these industries, potentially leading to higher unemployment rates and limited job prospects, furthering social inequality and economic instability.
Loss of Humanity’s Unique Skills
Lack of Empathy and Emotional Intelligence in AI
AI’s inability to genuinely empathize and comprehend human emotions poses a fundamental concern. While AI systems can simulate emotions and mimic human interactions to some extent, they lack the inherent understanding and depth of emotional intelligence that humans possess. This can limit their ability to effectively respond to complex emotional situations, especially in contexts where human empathy and connection are crucial.
Diminished Value of Human Expertise
Additionally, the rapid progress of AI may result in the diminished value of human expertise. As AI systems become more capable and efficient at performing complex tasks, there is a risk that human skills and expertise may be overshadowed. The unique knowledge and experiences that humans bring to various fields may be devalued, potentially leading to a loss of diversity and richness in problem-solving and decision-making processes.
Reduction in Manual Skills and Craftsmanship
The automation enabled by AI also poses a risk to manual skills and craftsmanship. Industries that rely on manual labor and traditional artisanal craftsmanship may witness a decline as AI-powered systems take over these tasks. While automation can enhance efficiency and productivity, it risks diminishing the artistry and skill that humans bring to these crafts, impacting cultural heritage and craftsmanship traditions in the process.
Dependency Risks
Over-reliance on AI Systems
As AI systems become increasingly prevalent and sophisticated, there is a risk of over-reliance on these systems. The assumption that AI can handle all tasks flawlessly can lead to complacency and reduced vigilance. In critical sectors such as healthcare or transportation, blind trust in AI without human oversight and intervention can have severe consequences, including compromising safety, ethics, and overall system resilience.
Vulnerability to Cyber Attacks
The integration of AI systems in various domains exposes them to the vulnerabilities and risks associated with cyber attacks. Hackers and malicious actors may exploit weaknesses in AI models or systems, potentially causing significant damage and disruption. Ensuring robust cybersecurity measures, continuous monitoring, and regular updates become essential to safeguarding AI systems and minimizing the risks from cyber threats.
Disruptive Impacts of AI Failures
Another consideration is the potential for disruptive impacts when AI systems fail. Whether due to technical glitches, algorithmic biases, or unforeseen circumstances, failures can have widespread repercussions. System failures in critical infrastructure, financial markets, or autonomous vehicles can pose significant risks to public safety, financial stability, and overall societal well-being, emphasizing the need for comprehensive risk management and contingency plans.
Unemployment Challenges
Inadequate Job Market Adaptations
As AI technology evolves, there is a need for the job market to adapt to the changing landscape. However, inadequate preparations and policies may result in significant unemployment challenges. The displacement of workers and the emergence of new roles requiring different skill sets necessitate proactive measures such as retraining programs and fostering a supportive environment for reskilling and upskilling efforts.
Job Market Polarization
Moreover, the impact of AI on the job market can lead to polarization. While some industries may experience job growth and increased demand for specialized AI-related roles, others may witness significant job losses. This polarization can create challenges for individuals transitioning from declining industries to emerging ones, potentially leading to imbalances in the labor market and contributing to social and economic inequalities.
Retraining and Upskilling Challenges
The effectiveness and accessibility of retraining and upskilling programs are crucial in addressing the unemployment challenges posed by AI. The rapid pace of AI advancements and the evolving skill requirements may create difficulties for individuals seeking to acquire the necessary knowledge and abilities. Overcoming these challenges requires collaboration between governments, educational institutions, and industry stakeholders to establish comprehensive and inclusive programs that empower individuals to adapt to the changing job market.
Potential for Autonomous Weapons
Military Application Risks
The potential use of AI in military applications raises concerns about the ethical implications and risks associated with autonomous weapons. Autonomous weapons systems equipped with AI have the potential to make decisions on their own, potentially leading to unintended consequences or escalating conflicts. The lack of human decision-making in critical situations demands careful consideration and robust frameworks to ensure responsible and ethical use of AI technologies in the military context.
Lack of Human Decision-Making in Critical Situations
The absence of human decision-making in critical situations involving autonomous weapons poses significant challenges. The reliance on AI algorithms for determining targets, engagement, or even the use of force raises questions about accountability and ethical responsibility. Ensuring appropriate human oversight and control mechanisms becomes crucial to prevent the misuse or excessive delegation of authority to AI systems in military contexts.
Potential Escalation of Conflicts
The deployment of autonomous weapons has the potential to escalate conflicts due to the speed and precision at which these systems can operate. The absence of human judgment and understanding of complex geopolitical dynamics can amplify the risks of unintended consequences and miscalculations. Careful regulation, international cooperation, and adherence to ethical frameworks are necessary to prevent the potential escalation of conflicts fueled by AI-infused military capabilities.
In conclusion, while AI presents various benefits and potential for societal progress, it also poses significant concerns and challenges. From job displacement and ethical concerns regarding transparency and bias to dehumanization and the risks associated with dependency and unemployment, the negative impacts of AI are widespread and multifaceted. Ensuring responsible and ethical development, implementation, and governance of AI systems is crucial to mitigate these concerns and maximize the benefits AI can offer while safeguarding human well-being and societal values.