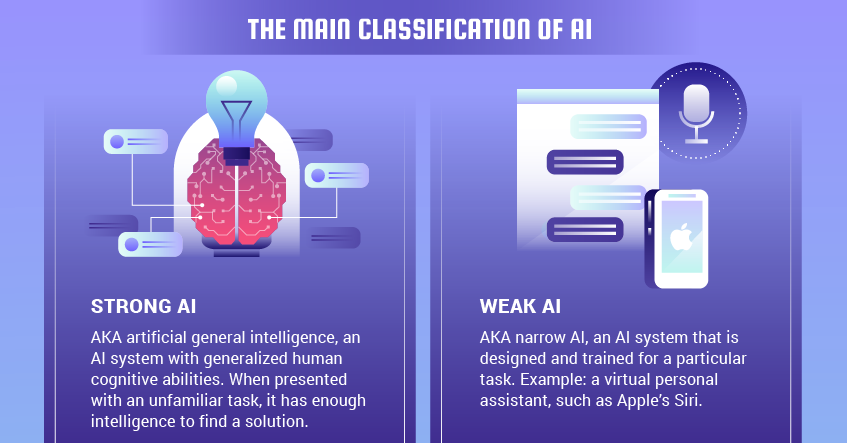
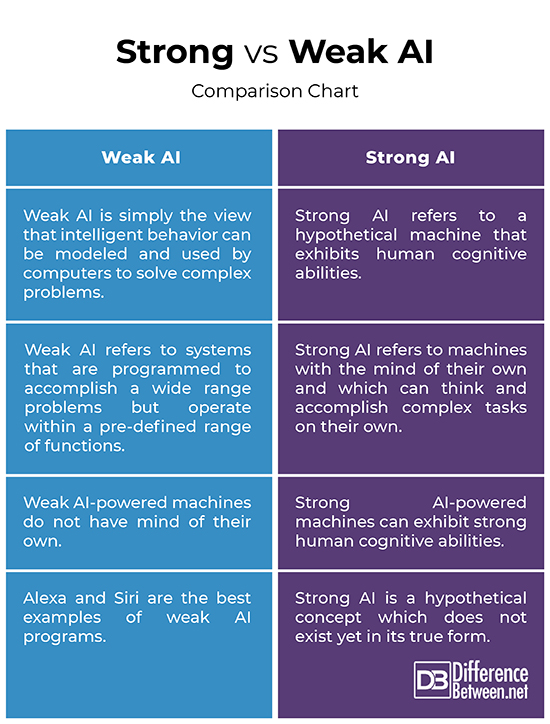
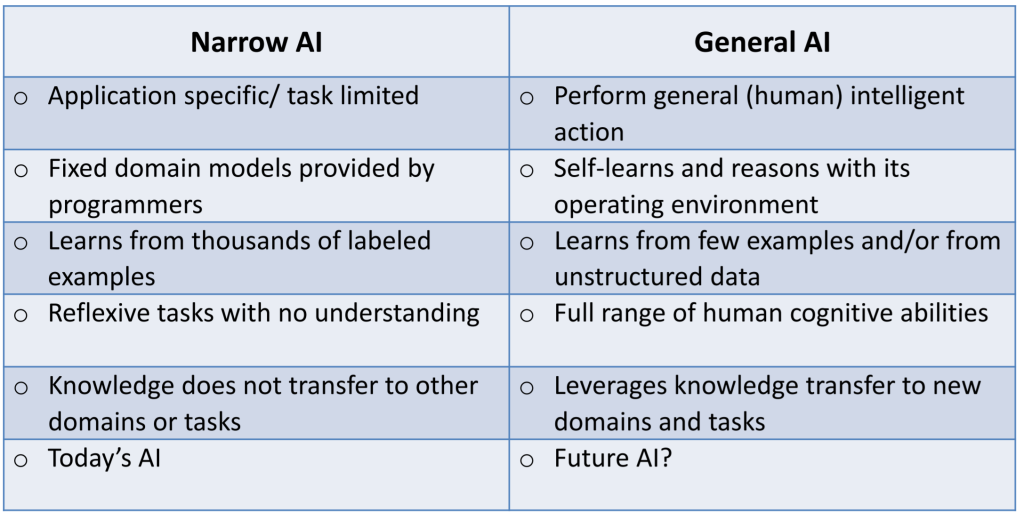
AI, or artificial intelligence, has quickly become a game-changer in various industries, offering businesses a myriad of benefits. In this article, we will explore the top three advantages that AI can bring to your business. From improved productivity and streamlined processes to better decision-making and enhanced customer experiences, AI has the potential to revolutionize the way you operate and boost your bottom line. So, strap in and get ready to discover how AI can take your business to new heights.

Increased Efficiency and Productivity
Automated Processes
Implementing artificial intelligence (AI) in your business can lead to increased efficiency and productivity. By automating repetitive tasks, AI frees up valuable time and resources that can be redirected towards more strategic initiatives. For example, customer service inquiries can be handled by AI-powered chatbots, eliminating the need for manual intervention and allowing your employees to focus on more complex customer issues. With AI technology, you can streamline your processes and ensure that tasks are completed accurately and efficiently.
Streamlined Operations
AI can also contribute to streamlined operations within your business. With the ability to analyze large amounts of data in real-time, AI algorithms can identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies in your processes. By pinpointing areas for improvement, you can optimize your operations and reduce unnecessary costs. For instance, AI-enabled systems can analyze production data to identify areas of waste and suggest improvements to increase productivity. This allows you to streamline your operations and enhance overall efficiency.
Real-Time Decision Making
In today’s fast-paced business environment, making timely and informed decisions is crucial. AI technologies provide real-time insights and analytics, empowering businesses to make data-driven decisions on the spot. AI algorithms can analyze complex data sets and patterns, enabling businesses to spot trends and make accurate predictions about future outcomes. With real-time decision-making capabilities, you can respond quickly to changing market conditions, identify potential risks, and seize opportunities before your competitors. This not only increases your efficiency but also helps drive business growth and success.
Cost Reduction
Automation of Repetitive Tasks
One of the key benefits of AI in business is the automation of repetitive tasks. By leveraging AI technology, you can reduce the time and effort required to complete routine tasks, such as data entry, inventory management, or invoice processing. This automation not only saves valuable employee time but also minimizes human error, leading to increased accuracy and reduced rework. By automating these tasks, you can cut costs associated with manual labor, increase operational efficiency, and ultimately improve your bottom line.
Improved Resource Allocation
AI can also help businesses optimize resource allocation. By analyzing historical data and patterns, AI algorithms can predict future demand and consumption patterns. This allows you to allocate resources such as inventory, workforce, and production capacity more effectively, avoiding unnecessary excesses or shortages. With improved resource allocation, you can minimize waste, reduce costs, and ensure that your business operates at optimal efficiency.
Reduced Human Error
Human error is an inherent risk in any business. However, AI can help mitigate this risk by automating processes and reducing reliance on manual intervention. AI systems are not prone to fatigue, distractions, or biases, resulting in improved accuracy and reduced errors. Whether it’s in customer service interactions or financial calculations, AI can provide consistent and error-free execution of tasks. By minimizing human error, you can avoid costly mistakes, enhance quality control, and protect your reputation.
Enhanced Customer Experience
Personalized Recommendations
AI-powered recommendation engines can significantly enhance the customer experience. By analyzing customer data, purchase history, and behavior patterns, AI algorithms can provide personalized product or content recommendations tailored to each individual’s preferences. This level of personalization not only improves customer satisfaction but also increases the likelihood of sales and customer retention. By leveraging AI for personalized recommendations, you can create a more engaging and tailored experience for your customers, leading to increased loyalty and brand advocacy.
Advanced Chatbots
Chatbots, powered by AI, have revolutionized customer service by providing instant and personalized assistance. AI chatbots can understand natural language, interpret inquiries, and provide accurate and timely responses. They can handle a wide range of customer queries, from product inquiries to billing issues, without the need for human intervention. This not only improves response time but also frees up your customer service agents to focus on more complex tasks. By incorporating advanced chatbot technology into your customer service strategy, you can enhance the overall customer experience and foster customer satisfaction.
Improved Response Time
In today’s fast-paced world, customers expect quick and efficient service. AI technologies enable businesses to achieve faster response times by automating processes and providing real-time support. AI systems can analyze customer queries and provide instant responses, reducing wait times and ensuring prompt resolution of issues. Whether it’s through chatbot interactions or AI-powered self-service options, you can provide your customers with the convenience and speed they desire. By improving response time, you can enhance customer satisfaction, build brand loyalty, and gain a competitive edge in the market.

Data Analysis and Insights
Pattern Recognition
AI’s ability to analyze vast amounts of data quickly and accurately enables businesses to identify valuable patterns and trends. By recognizing these patterns, businesses can gain insights into customer preferences, market trends, and operational patterns. With AI-driven pattern recognition, you can uncover hidden opportunities, optimize marketing strategies, and improve operational efficiencies. This valuable insight allows businesses to make informed decisions based on data and maximize their chances of success.
Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics is a powerful application of AI that can help businesses forecast future outcomes based on historical data. By analyzing patterns, AI algorithms make predictions about customer behavior, market trends, and demand levels. This allows businesses to proactively adjust their strategies, allocate resources appropriately, and make accurate forecasts. With predictive analytics, you can anticipate market changes, optimize your supply chain, and stay one step ahead of the competition.
Better Business Decisions
AI provides businesses with data-driven insights that can inform and improve decision-making processes. By leveraging AI algorithms, businesses can analyze complex data sets and gain a deeper understanding of their operations, customers, and market dynamics. This enables more informed decision-making, as AI algorithms can provide objective insights, identify risks, and evaluate potential outcomes. With AI-driven decision support, businesses can make better strategic choices, optimize resource allocation, and ultimately drive long-term success.
Competitive Advantage
Market Predictions and Trends
AI technology enables businesses to analyze market trends and predict future outcomes. By leveraging machine learning algorithms, businesses can analyze vast amounts of data, including competitor strategies, consumer behavior, and market conditions. This analysis enables businesses to make accurate predictions about future market trends, giving them a competitive advantage. By staying ahead of emerging trends, you can adapt your strategies, develop innovative products, and position your business as a market leader.
Efficient Competitive Analysis
AI-powered tools can significantly streamline the process of competitive analysis. These tools can collect and analyze data from a variety of sources, including competitor websites, social media platforms, and industry reports. By automating the data collection and analysis process, businesses can save valuable time and resources. AI algorithms can identify key competitive insights, such as pricing trends, product features, or marketing strategies, allowing businesses to make informed decisions and develop effective competitive strategies.
Innovation and Agility
AI can foster innovation and agility within businesses by enabling faster and more efficient processes. By automating repetitive tasks and providing real-time insights, AI frees up valuable resources and allows employees to focus on innovative and strategic initiatives. With AI-driven innovation, businesses can develop new products, improve existing ones, and stay ahead of changing market demands. By embracing AI technology, businesses can enhance their agility, adapt to market changes, and maintain a competitive edge.
Improved Cybersecurity
Advanced Threat Detection
As cyber threats become increasingly sophisticated, businesses need robust cybersecurity measures to protect their sensitive data. AI technologies can play a crucial role in identifying and mitigating these threats. AI systems can continuously monitor network traffic, detect anomalies, and proactively respond to potential security breaches. By leveraging AI for threat detection, businesses can strengthen their cybersecurity defenses, reduce the risk of data breaches, and protect their valuable assets.
Real-Time Monitoring
AI enables real-time monitoring of cybersecurity events, providing businesses with immediate alerts and responses to potential threats. AI algorithms can analyze network logs, user behavior, and system events to identify suspicious activities and potential security breaches. Real-time monitoring allows businesses to respond swiftly to threats, minimizing the impact of security incidents and ensuring continuous protection. By harnessing AI for real-time cybersecurity monitoring, businesses can enhance their security posture and safeguard their critical information.
Vulnerability Management
Identifying and addressing vulnerabilities is a key aspect of effective cybersecurity. AI technologies can automate vulnerability assessments, scanning systems and applications to identify potential weaknesses. AI algorithms can then prioritize vulnerabilities based on their severity and potential impact, helping businesses allocate resources efficiently for remediation. By leveraging AI for vulnerability management, businesses can stay ahead of potential threats, reduce the risk of security breaches, and protect their valuable digital assets.
Optimized Supply Chain Management
Demand Forecasting
AI can optimize supply chain management by providing accurate demand forecasting. By analyzing historical data, market trends, and customer behavior, AI algorithms can predict future demand levels with high accuracy. With this insight, businesses can plan their production, inventory, and distribution strategies more effectively, reducing stockouts and overstock situations. By leveraging AI for demand forecasting, businesses can optimize their supply chain, minimize costs, and increase customer satisfaction.
Inventory Management
Efficient inventory management is crucial for businesses to avoid excess stock or shortage situations. AI technologies can analyze data in real-time and provide insights into inventory levels, supplier lead times, and demand patterns. This enables businesses to optimize their inventory levels, reducing carrying costs and improving overall efficiency. By leveraging AI for inventory management, businesses can ensure they have the right products in stock at the right time, improving customer satisfaction and reducing operational costs.
Route Optimization
AI algorithms can optimize logistical operations by providing efficient route planning and optimization strategies. By analyzing factors such as traffic conditions, delivery constraints, and fuel costs, AI-powered systems can determine the most optimal routes for product delivery. Route optimization reduces transportation costs, improves delivery speed, and enhances overall supply chain efficiency. By leveraging AI for route optimization, businesses can maximize their operational efficiency and deliver products to customers in a timely manner.
Employee Empowerment
Automated Employee Support
AI technologies can provide automated support to employees, reducing their workload and enabling them to focus on more strategic tasks. For example, AI-powered chatbots can answer frequently asked questions, provide on-demand training, and assist in troubleshooting issues. By automating these support functions, businesses can enhance employee productivity, reduce response times, and improve overall satisfaction. Moreover, AI-powered virtual assistants can streamline administrative tasks, such as scheduling meetings or managing emails, giving employees more time to focus on value-added activities.
Enhanced Decision-Making Support
AI technologies can empower employees with real-time data and insights, enabling them to make informed decisions. AI algorithms can analyze complex data sets and provide employees with relevant information and recommendations. This supports employees in strategic decision-making processes by providing them with insights that would otherwise be time-consuming to gather manually. By leveraging AI for decision-making support, businesses can enhance employee capabilities, improve decision quality, and drive better business outcomes.
Reduced Workload
By automating repetitive and mundane tasks, AI can significantly reduce the workload of employees. AI technologies can handle tasks such as data entry, invoice processing, or report generation, freeing up employee time for more complex and critical tasks. This not only improves employee satisfaction but also allows them to focus on tasks that require creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving skills. By leveraging AI to reduce employee workload, businesses can create a more efficient and fulfilling work environment, ultimately leading to increased productivity and employee retention.
Streamlined HR Processes
Automated Recruitment and Onboarding
AI can streamline various HR processes, starting from recruitment and onboarding. AI technologies can analyze candidate resumes, conduct initial screenings, and even conduct automated video interviews, reducing the time and effort required to identify qualified candidates. Additionally, AI can automate the onboarding process by providing new employees with relevant information, training materials, and necessary forms. By leveraging AI for recruitment and onboarding, businesses can streamline these processes, improve efficiency, and enhance the overall candidate and employee experience.
Efficient Employee Performance Evaluation
AI technologies can facilitate more efficient and objective employee performance evaluations. By leveraging AI algorithms, businesses can collect and analyze performance data, providing managers with comprehensive insights into employee capabilities, achievements, and areas for development. AI-powered performance evaluation tools can remove biases, enhance accuracy, and provide a consistent framework for evaluating employees. By streamlining the performance evaluation process, businesses can improve employee feedback, enhance their development opportunities, and ultimately drive employee engagement and satisfaction.
Data-Driven Hiring Decisions
AI can enable data-driven hiring decisions by analyzing vast amounts of data to identify candidates with the highest potential for success. AI algorithms can compare candidate attributes, skills, and previous performance against desired criteria, providing a more objective assessment of their suitability for a particular role. By leveraging AI for hiring decisions, businesses can reduce biases, improve the quality of hires, and make more informed decisions based on data. This enables businesses to build a talented and diverse workforce, driving innovation and long-term success.
Improved Risk Management
Early Detection of Fraudulent Activity
AI technologies can help businesses detect and mitigate fraudulent activities at an early stage. By analyzing patterns, outliers, and anomalies in data, AI algorithms can identify potential fraudulent transactions, cybersecurity breaches, or suspicious behavior. This early detection enables businesses to take immediate action to prevent or limit the impact of fraudulent activities, safeguarding their assets and reputation. By leveraging AI for risk management, businesses can enhance their fraud detection capabilities, reduce financial losses, and protect the trust of their customers and stakeholders.
Enhanced Compliance Monitoring
Compliance with regulations and industry standards is a significant concern for businesses. AI can enhance compliance monitoring by automating the analysis of vast amounts of data to identify potential compliance violations. AI algorithms can quickly search and flag inconsistencies, ensuring that businesses adhere to applicable laws and regulations. By leveraging AI for compliance monitoring, businesses can reduce the risk of penalties and legal issues, ensuring their operations align with ethical and legal standards.
Risk Prediction and Mitigation
AI technologies can enable proactive risk management by predicting potential risks and providing mitigation strategies. By analyzing historical data, market trends, and external factors, AI algorithms can identify emerging risks and anticipate their potential consequences. This allows businesses to implement proactive measures to mitigate risks, adjust their strategies, and protect their operations. By leveraging AI for risk prediction and mitigation, businesses can stay ahead of potential threats, reduce potential damages, and ensure business continuity.
In conclusion, implementing AI in your business can bring numerous benefits across various aspects of your operations. From increased efficiency and productivity through automated processes and real-time decision-making to enhanced customer experience through personalized recommendations and advanced chatbots, AI technologies have the potential to transform your business. Additionally, AI can provide valuable data analysis and insights, strengthen your competitive advantage, improve cybersecurity, optimize supply chain management, empower your employees, streamline HR processes, and enhance risk management capabilities. By harnessing the power of AI, businesses can unlock new opportunities, drive growth, and stay ahead in the increasingly competitive business landscape.