So you’re curious about the different types of artificial intelligence (AI) and which one is the most widely used, huh? Well, buckle up because we’re about to take a closer look at the AI landscape. From machine learning and natural language processing to computer vision and expert systems, there are numerous AI techniques out there. But which type reigns supreme when it comes to applications in various industries? Let’s find out!
Introduction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is an ever-evolving field that has revolutionized various industries, from healthcare to finance. In this article, we will explore the different types of AI and delve into their applications and functionalities. Whether you are familiar with AI or just getting started, this article will provide a comprehensive overview of supervised learning, unsupervised learning, reinforcement learning, natural language processing (NLP), computer vision, expert systems, neural networks, deep learning, genetic algorithms, and fuzzy logic.
Supervised Learning
Supervised learning is a popular type of AI that involves training a machine learning model with labeled data. It requires a well-defined dataset where the input features and corresponding output labels are provided. With this information, the model learns the patterns and relationships between the input and output and can predict the correct label for new, unseen data. Supervised learning is widely used in tasks such as sentiment analysis, fraud detection, and spam filtering.
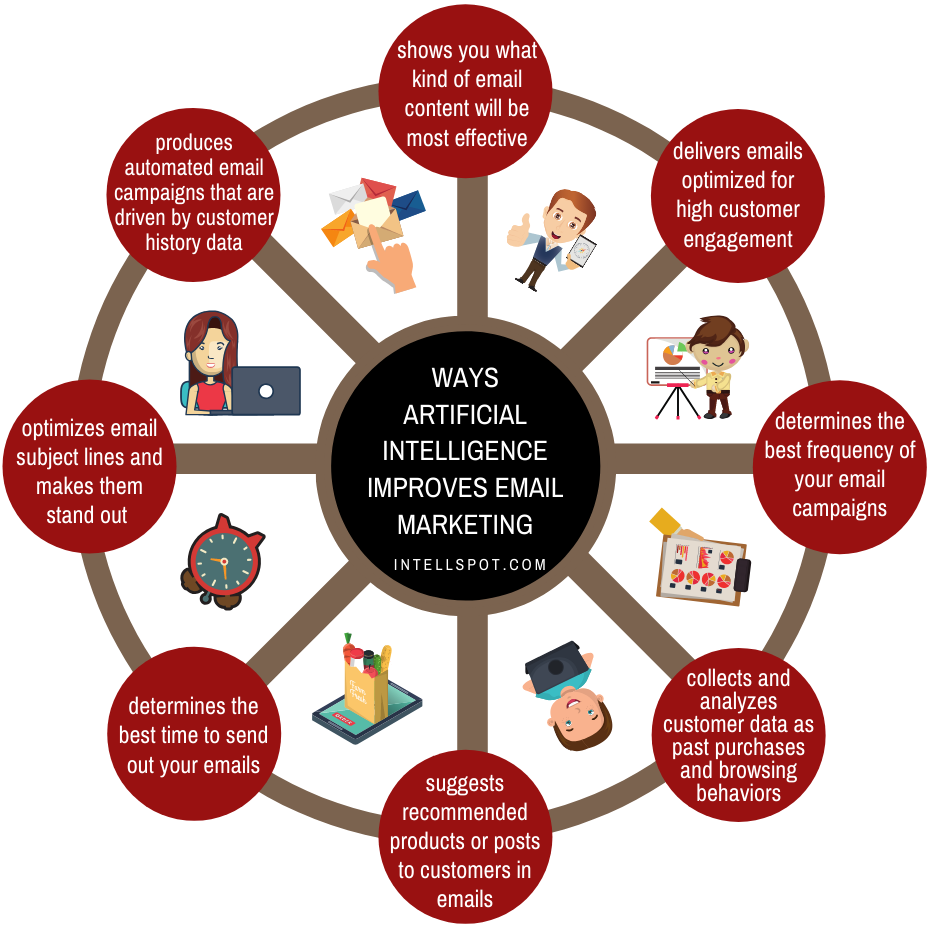
This image is property of digitalmarketingcommunity.com.
Unsupervised Learning
Unlike supervised learning, unsupervised learning does not require labeled data for training. Instead, it focuses on discovering patterns, relationships, or structures within the data on its own. This type of AI is particularly useful when dealing with large datasets where manually labeling the data would be time-consuming or impractical. Unsupervised learning techniques, such as clustering and dimensionality reduction, can be applied to various domains, including customer segmentation, anomaly detection, and recommendation systems.
Reinforcement Learning
Reinforcement learning is a type of AI that involves an agent learning to make decisions by interacting with an environment. It operates under a reward-based system, where the agent receives positive or negative feedback based on its actions. The goal of reinforcement learning is to maximize the cumulative reward over time, and the agent learns to take actions that lead to desirable outcomes while avoiding unfavorable ones. This type of AI is commonly applied in robotics, game playing (such as AlphaGo), and autonomous vehicle control.
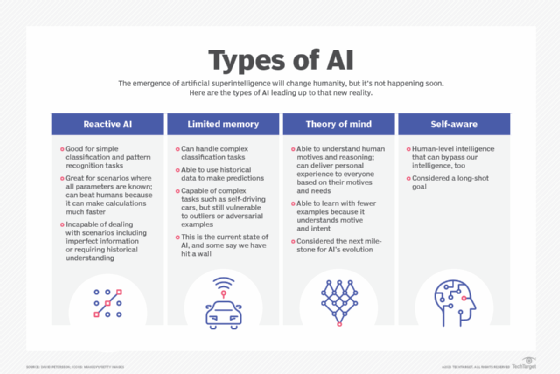
This image is property of cdn.ttgtmedia.com.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is a subfield of AI that focuses on the interaction between computers and human language. It enables computers to understand, interpret, and generate human language in a meaningful way. NLP has numerous applications, and two key areas within it are text classification and language translation.
Text Classification
Text classification is the process of categorizing text documents into different predefined classes or categories. It enables systems to automatically analyze and classify large volumes of textual data, making it valuable in sentiment analysis, topic identification, and spam detection. This type of AI is used in various industries, including marketing, customer service, and content filtering.
Language Translation
Language translation is another essential application of NLP that focuses on automatically translating text or speech from one language to another. With advancements in machine learning and deep learning techniques, language translation has improved significantly. It has become easier to bridge communication gaps between different language speakers, making it invaluable for industries such as travel, e-commerce, and international diplomacy.
Speech Recognition
Speech recognition is the ability of a computer system to recognize and convert spoken words into written text. This technology has experienced remarkable progress in recent years, enabling virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa to understand and respond to human speech accurately. Speech recognition has diverse applications, including transcription services, voice-controlled devices, and accessibility tools for individuals with disabilities.
Computer Vision
Computer vision is an area of AI that focuses on enabling computers to understand and interpret visual content from images or videos. It aims to replicate human visual perception and extract meaningful information from visual data. Computer vision finds applications in various fields, including self-driving cars, surveillance systems, and medical imaging.
Object Detection
Object detection is a computer vision task that involves identifying and localizing objects within an image or video. It goes beyond simple image classification by providing not only the label of the object but also its precise location within the scene. Object detection is crucial in autonomous vehicles, facial recognition, and object tracking applications.
Image Classification
Image classification is a computer vision task that involves assigning a label or a predefined category to an image. It enables machines to recognize and categorize images based on their visual contents. Image classification has numerous applications, including medical image analysis, quality control in manufacturing, and content filtering in social media.
Facial Recognition
Facial recognition is a computer vision technology that focuses on identifying and verifying individuals based on their facial features. It analyzes unique facial patterns and compares them to an existing database to determine a person’s identity. Facial recognition has applications in security systems, access control, and law enforcement.
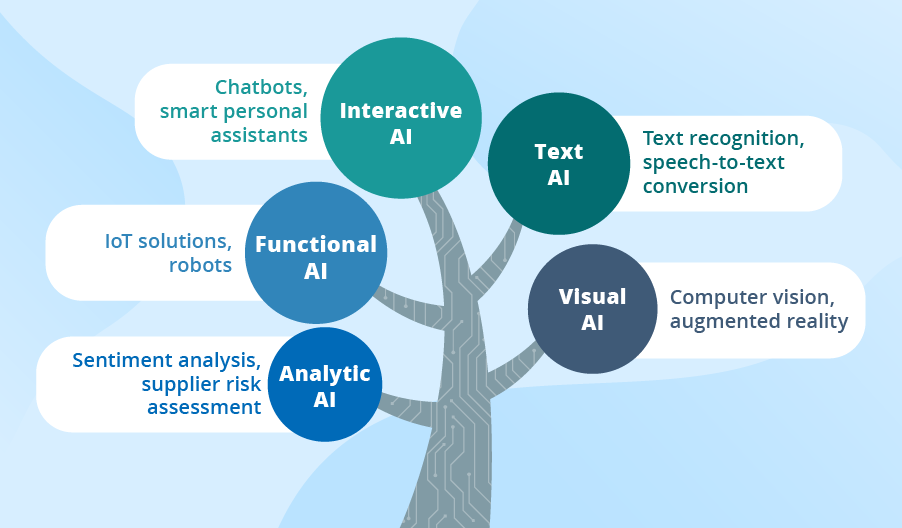
This image is property of www.scnsoft.com.
Expert Systems
Expert systems are a type of AI that emulates the decision-making abilities of human experts in a specific domain. They are rule-based systems that rely on knowledge bases and reasoning engines to provide intelligent advice or solutions. Expert systems have been widely used in fields such as healthcare diagnosis, financial planning, and troubleshooting complex technical issues.
Neural Networks
Neural networks are computational models inspired by the structure and functioning of the human brain. They consist of interconnected artificial neurons that process and transmit information. Neural networks are at the core of many AI applications and can be categorized into different types based on their architectural design and functionality.
Feedforward Neural Networks
Feedforward neural networks are the simplest type of neural networks, consisting of layers of interconnected neurons where the information flows in a single direction. They are commonly used in tasks such as pattern recognition, regression, and classification.
Convolutional Neural Networks
Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) are specialized neural networks for analyzing visual data. They are particularly effective in tasks such as image recognition, object detection, and image segmentation. CNNs utilize convolutional layers and pooling layers to capture spatial hierarchies in images.
Recurrent Neural Networks
Recurrent neural networks (RNNs) are designed to handle sequential data, such as time series or natural language. RNNs have connections that can retain information across different time steps, making them suitable for tasks like speech recognition, machine translation, and sentiment analysis.
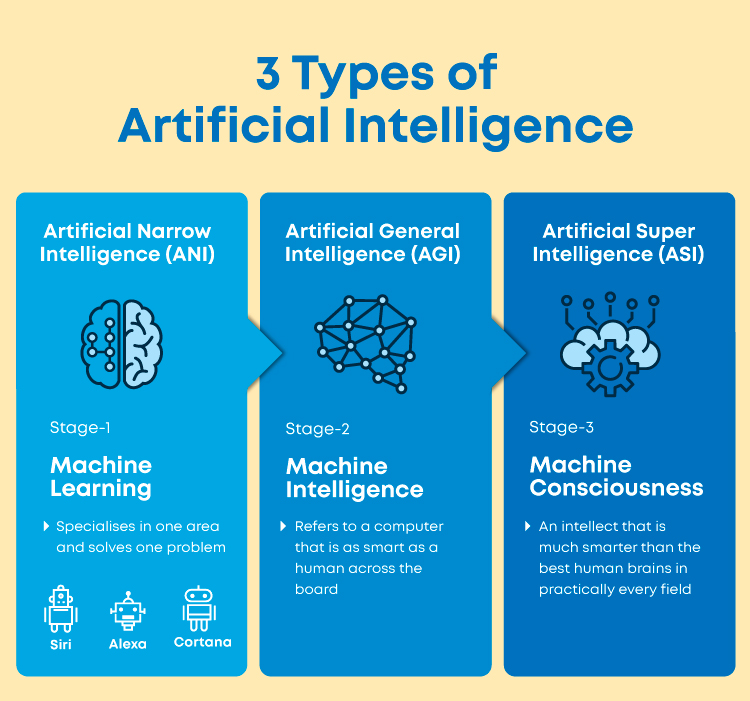
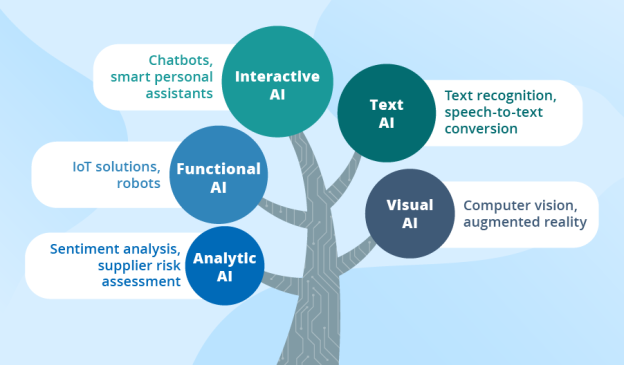
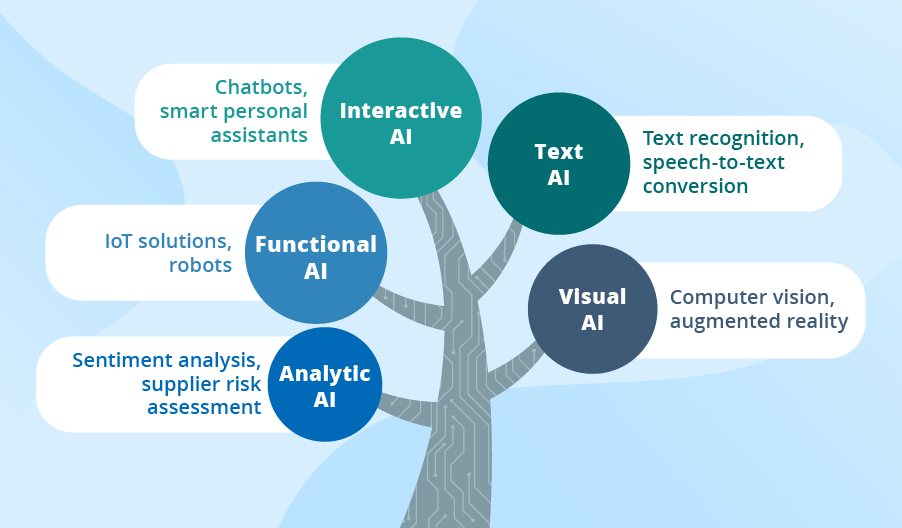
This image is property of d1m75rqqgidzqn.cloudfront.net.
Deep Learning
Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that focuses on training deep neural networks with multiple layers. It leverages the power of large neural networks and vast amounts of data to learn complex patterns and representations. Deep learning has revolutionized many AI applications, including image and speech recognition, natural language processing, and autonomous vehicles.
Genetic Algorithms
Genetic algorithms are a type of AI that is inspired by the process of natural selection and evolutionary biology. They are optimization algorithms that use a population of potential solutions and iteratively improve them over generations. Genetic algorithms have been used in various domains, such as scheduling, engineering design, and financial portfolio optimization.
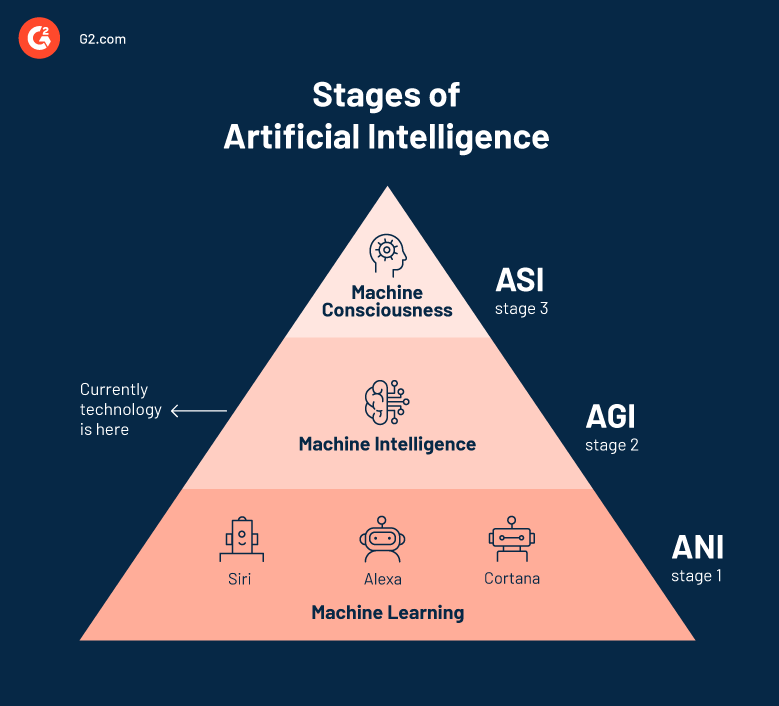
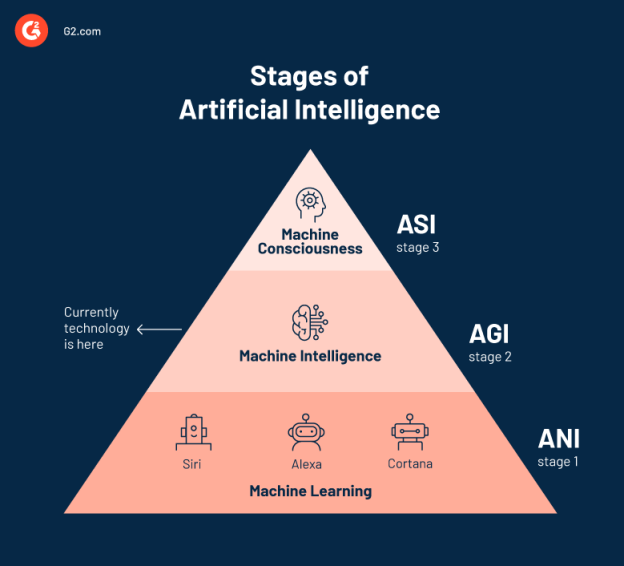
This image is property of learn.g2.com.
Fuzzy Logic
Fuzzy logic is a form of logic that goes beyond traditional binary (true/false) logic and allows for degrees of truth. Instead of precise values, it deals with concepts of uncertainty and ambiguity. Fuzzy logic has found applications in areas such as control systems, decision-making, and artificial intelligence. It is particularly useful when dealing with imprecise or incomplete information.
Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence encompasses a broad range of techniques and methodologies, each with its own unique applications and strengths. From supervised learning to fuzzy logic, AI has permeated nearly every aspect of our lives, enabling machines to perform tasks that were once thought to be exclusive to human intelligence. As AI continues to advance, it holds the promise of transforming industries, improving efficiency, and enhancing our daily lives. Whether it’s helping doctors diagnose diseases, enabling autonomous vehicles to navigate safely, or making language translation seamless, the impact of AI is undeniable and will only continue to grow.