So you’ve heard all about the countless benefits of AI in marketing – increased efficiency, personalized customer experiences, and data-driven insights. But have you ever stopped to consider the flip side? In this article, we’ll take a closer look at the drawbacks of AI in marketing. From potential job losses to ethical concerns, we’ll explore the not-so-glamorous side of this technological marvel and shed light on the hidden disadvantages that marketers need to be aware of. So buckle up and get ready to uncover the potential pitfalls of AI in marketing.
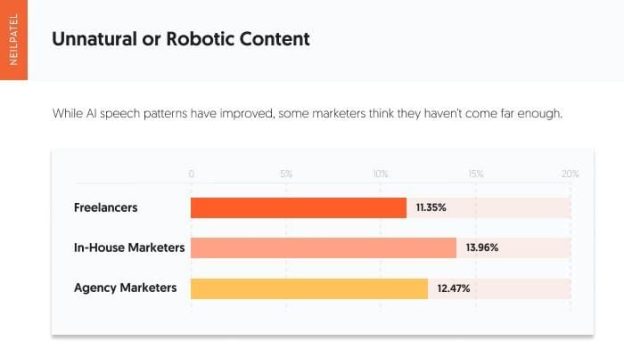
This image is property of neilpatel.com.
Lack of human touch
Reduced personalization
With the increased use of AI in marketing, there is a significant reduction in personalization. AI relies on algorithms and data analysis to understand customer preferences and behaviors, but it lacks the human touch that can truly connect with individual customers. While AI can segment customers into broad categories based on their demographics and past behavior, it often fails to capture the nuances and idiosyncrasies that make each customer unique. This lack of personalization can lead to generic and impersonal marketing messages that fail to resonate with customers on a deeper level.
Loss of emotional connection
Another drawback of AI in marketing is the loss of emotional connection between brands and customers. AI-powered marketing tools are designed to analyze data and make predictions based on patterns and trends. However, they lack the ability to understand and respond to human emotions in real-time. Emotional connections play a crucial role in building brand loyalty and long-term customer relationships. Without the empathetic understanding that humans possess, AI struggles to create meaningful emotional connections with consumers, leading to a sense of detachment and disengagement.
Potential for bias
Relying on biased data
One of the major concerns with AI in marketing is the potential reliance on biased data. AI algorithms learn from historical data to make predictions and recommendations. However, if the data used for training the algorithms is biased, it will undoubtedly lead to biased outcomes. For example, if an AI system is trained on data that primarily represents certain demographics or excludes certain underrepresented groups, it can perpetuate existing biases and discriminate against certain segments of the population. This can have serious ethical implications and undermine the goal of fair and equitable marketing practices.
Unintentional reinforcement of stereotypes
In addition to relying on biased data, AI in marketing can unintentionally reinforce stereotypes. When AI algorithms analyze vast amounts of data, they may identify patterns and correlations that are not necessarily accurate or fair. If these patterns are then used to make marketing decisions, it can lead to the perpetuation of stereotypes. For example, an AI system may associate certain products or services with specific gender roles or demographics based on faulty data analysis. This can further marginalize certain groups and limit their access to opportunities and resources.
Privacy concerns
Collection and use of personal data
AI-powered marketing often relies on the collection and use of personal data, which raises significant privacy concerns. As AI systems gather information about individuals’ habits, preferences, and behaviors, there is a risk of this data being misused or mishandled. Consumers may feel uncomfortable with the idea of their personal information being stored and analyzed by AI algorithms, especially if they are not fully aware of how their data is being used. This can erode trust between consumers and brands, leading to a reluctance to engage with AI-driven marketing initiatives.
Security risks
The increased reliance on AI in marketing also introduces new security risks. As AI systems collect and analyze vast amounts of data, they become attractive targets for cybercriminals and hackers. If these systems are not adequately protected, sensitive customer information can be compromised, leading to identity theft, fraud, and other malicious activities. The potential damage to a brand’s reputation and trustworthiness can be severe, and it becomes crucial for companies to invest in robust cybersecurity measures to mitigate these risks.
Difficulty in creativity and intuition
Limits in generating original ideas
One of the disadvantages of AI in marketing is its limited ability to generate truly original and creative ideas. While AI algorithms can analyze data and identify patterns, they lack the intuitive and imaginative capabilities of humans. Creativity often involves thinking outside the box and making unique connections, which can be challenging for AI systems that rely on predefined rules and algorithms. As a result, marketing campaigns driven solely by AI may lack the innovative spark that human marketers can bring.
Inability to understand complex human behavior
Humans have a unique understanding of complex human behavior, motivations, and emotions. AI, on the other hand, struggles to comprehend and respond to these intricacies accurately. Understanding human behavior is critical to effective marketing, as it allows marketers to tailor their strategies to the specific needs and desires of their target audience. AI may be able to analyze large datasets to identify general patterns, but it often falls short when it comes to understanding the underlying reasons and nuances behind human behavior. This limitation can lead to marketing campaigns that miss the mark and fail to resonate with consumers on a deeper level.

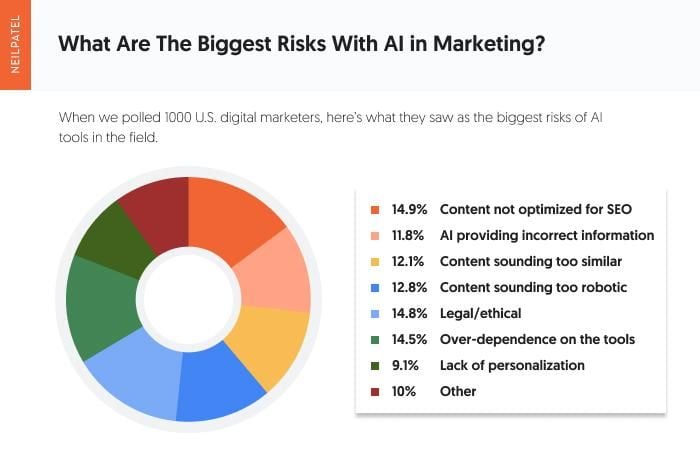
This image is property of pureseo.com.
Costly implementation
Investment in infrastructure
Implementing AI in marketing requires a significant investment in infrastructure. Companies need to invest in robust computing systems, storage capabilities, and network infrastructure to support AI-powered marketing initiatives. This infrastructure needs to handle large amounts of data and sophisticated algorithms, which can be cost-intensive to set up and maintain. Smaller businesses with limited resources may find it challenging to bear the initial costs of implementing AI, making it more accessible to larger corporations with substantial financial backing.
Training and maintenance expenses
In addition to infrastructure costs, training and maintenance expenses are also significant considerations in the implementation of AI in marketing. AI algorithms need continuous fine-tuning and updating to ensure optimal performance, which requires skilled professionals and ongoing investments in training programs. Hiring and retaining AI experts can be costly, especially considering the high demand for such professionals in the market. The long-term maintenance expenses of AI systems can add up, making it a significant financial commitment for businesses.
Lack of adaptability
Inability to handle unexpected situations
AI algorithms are designed to operate within predefined parameters and patterns. They excel in situations where the data is consistent and predictable. However, AI struggles when faced with unexpected situations or outliers that fall outside its learned patterns. This lack of adaptability can hinder AI-driven marketing campaigns from effectively responding to dynamic market conditions and sudden changes in consumer preferences. Human marketers possess the ability to think on their feet, adapt, and make quick strategic adjustments when faced with unforeseen circumstances, which is a key advantage that AI currently lacks.
Difficulty with rapidly changing marketing trends
Marketing trends and techniques are constantly evolving in response to consumer behavior, technological advancements, and market dynamics. AI systems may struggle to keep up with these rapidly changing trends. As AI algorithms rely on historical data for training, they may not be equipped to anticipate or adapt to emerging trends promptly. Human marketers are better positioned to stay aware of the latest trends and employ creative strategies and innovative approaches to seize new opportunities. The limitations of AI in quickly adapting to changing marketing trends can put businesses at a disadvantage in an increasingly competitive landscape.
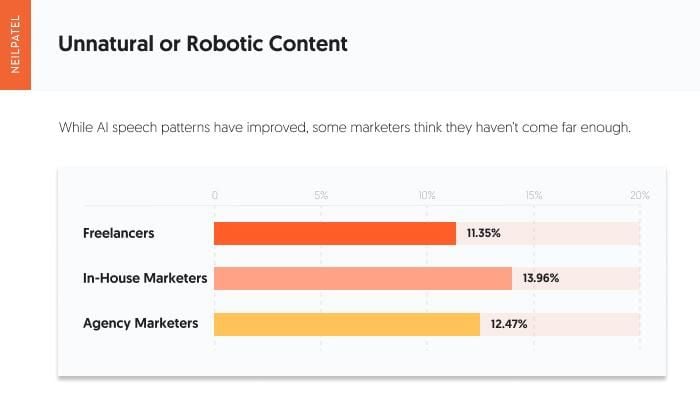
This image is property of neilpatel.com.
Risk of algorithmic errors
Performance decline with incorrect algorithms
The performance of AI in marketing heavily relies on the accuracy and quality of the underlying algorithms. If the algorithms used are flawed or incorrect, the entire AI system’s performance can suffer. Incorrect algorithms can lead to inaccurate predictions, inefficient targeting, and ineffective campaign optimization. This can result in wasted resources, poor return on investment, and diminished marketing outcomes. Continuous monitoring and validation of algorithms are necessary to mitigate the risk of errors and ensure the reliability and effectiveness of AI-powered marketing initiatives.
Misinterpretation of data
AI algorithms analyze vast amounts of data to generate insights and recommendations. However, the interpretation of data is not foolproof, and AI systems may misinterpret or misattribute causality based on correlations alone. Without a clear understanding of the context and nuances surrounding the data, AI can make faulty predictions and decisions. This misinterpretation of data can have serious repercussions in marketing, as companies may base their strategies on inaccurate insights, leading to suboptimal outcomes. It highlights the importance of human oversight and critical thinking in validating and interpreting AI-generated insights.
Dependency on data availability
Reliance on quality and availability of data
The effectiveness of AI in marketing is heavily dependent on the quality and availability of data. AI algorithms require access to large, diverse, and high-quality datasets to make accurate predictions and recommendations. However, obtaining such data can be a challenging task. Limited or biased datasets can compromise the accuracy and fairness of AI-generated insights and hinder marketing effectiveness. Furthermore, companies that lack the resources or access to comprehensive data may be at a disadvantage, leading to a potential gap between large corporations with extensive data access and smaller businesses with limited resources.
Data-driven decision making
While data-driven decision making can bring valuable insights, it can also lead to a dependency on data at the expense of intuition and human judgment. AI in marketing often prioritizes quantifiable data and measurable metrics, potentially neglecting the qualitative aspects of marketing strategies. The human element in marketing, such as intuition, instinct, and experience, cannot be fully replaced by AI. Over-reliance on data can limit the ability to identify opportunities that may not be apparent in the numbers and can hinder the creative and strategic decision-making process.

This image is property of neilpatel.com.
Loss of jobs and human interaction
Automation leading to job displacement
One of the most significant concerns related to AI in marketing is the potential loss of jobs due to automation. As AI systems become more sophisticated, they can take over repetitive and routine tasks that were previously performed by humans, such as data analysis, content generation, and customer segmentation. While automation can lead to increased efficiency and productivity, it can also result in job displacement and unemployment for marketing professionals who are not able to adapt to the changing landscape. This can have profound socio-economic implications and necessitate the need for upskilling and retraining programs.
Reduced customer service experience
AI-powered marketing often relies on chatbots and automated customer service systems to handle customer inquiries and support. While these systems can provide quick responses and handle basic queries efficiently, they lack the warmth, empathy, and personal touch that human interactions offer. Customer service experiences driven solely by AI can come across as impersonal and cold, leading to a diminished customer experience. Building genuine connections and resolving complex issues often require the human element, as human customer service representatives can actively listen, empathize, and provide personalized solutions that AI-based systems cannot replicate.
Ethical concerns
Unintentional manipulation of consumer behavior
The use of AI in marketing raises ethical concerns regarding the unintentional manipulation of consumer behavior. AI algorithms can analyze consumer data to identify patterns and preferences, allowing companies to target specific individuals with tailored marketing content. However, this level of targeted marketing can potentially exploit vulnerabilities and manipulate consumer behavior without their awareness or consent. The line between personalization and manipulation can be thin, and companies must ensure that their AI-driven marketing practices prioritize transparency, informed consent, and ethical considerations.
Lack of moral decision-making ability
AI systems lack moral decision-making abilities that humans possess. While AI can analyze data and make predictions, it cannot understand or make moral judgments about the implications of its actions. This can lead to ethical dilemmas in marketing, as AI may unknowingly engage in practices that are considered morally wrong or unethical. It is essential for companies to exercise caution and ensure that they incorporate human oversight and ethical guidelines when deploying AI in marketing to prevent unintended ethical breaches.
In conclusion, while AI has brought significant advancements in marketing, there are several disadvantages that need to be carefully considered. The lack of human touch and emotional connection, potential for bias and reinforcement of stereotypes, privacy concerns, difficulty in creativity and intuition, costly implementation, lack of adaptability, risk of algorithmic errors, dependency on data availability, loss of jobs and human interaction, and ethical concerns are prominent challenges associated with AI in marketing. Understanding these disadvantages is crucial for businesses to strike a balance between leveraging the power of AI and maintaining a human-centric approach to marketing that respects individuality, privacy, and ethical considerations.
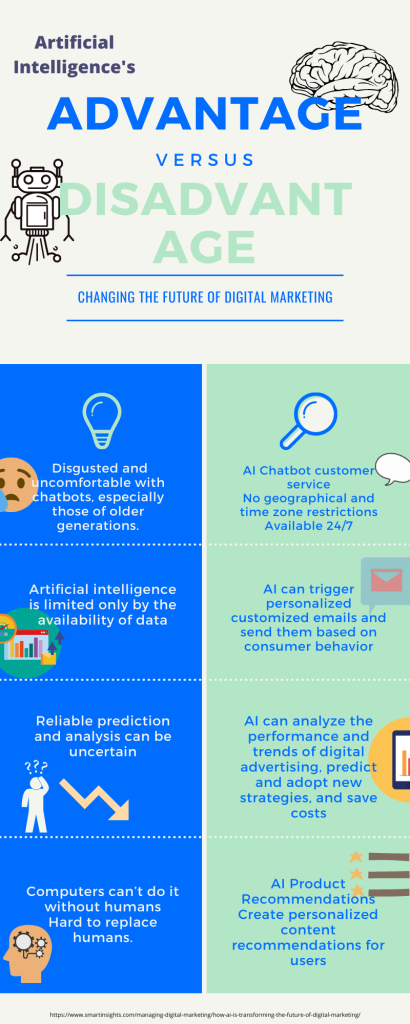
This image is property of miro.medium.com.